Trump’s Tariffs Reshape the US Tech Industry: Apple, Nvidia, and the Future of Global Trade

In recent years, the global landscape of international trade has been profoundly influenced by the tariff policies implemented under former President Donald Trump's administration. Aimed at reshaping the dynamics of trade between the United States and several global economic players, these tariffs primarily targeted Chinese imports, which have a direct bearing on the technology sector. The US tech industry, renowned for its global reach and heavy reliance on international supply chains, found itself at the heart of this trade war. Among the most significant companies impacted by these policies were two of the largest names in the tech world: Apple and Nvidia.
The US-China trade war, which intensified throughout Trump's presidency, introduced tariffs on billions of dollars of goods traded between the two countries. These tariffs were imposed under the pretext of protecting American jobs and reducing the trade deficit with China, a policy that had wide-ranging consequences across various industries. While the US tech sector has long been an engine for innovation, it is also heavily reliant on global supply chains. From hardware manufacturing to software development, the industry is tightly interwoven with international trade and production networks. As a result, the tariff policies altered the operating environment for companies like Apple and Nvidia, who faced challenges related to rising costs, disrupted supply chains, and shifting market demands.
At the core of the disruption were the tariffs on Chinese-made components, many of which are integral to the production of technology products. Apple, for example, sources a significant portion of its hardware from Chinese manufacturers, while Nvidia, a leading semiconductor company, relies on Chinese suppliers for critical components used in its cutting-edge GPUs. These tariffs had immediate cost implications, especially as both companies were forced to reassess their manufacturing strategies and seek alternatives to mitigate the financial strain.
Furthermore, the geopolitical tension between the US and China added another layer of complexity. As US companies like Apple and Nvidia navigated these challenges, they were also dealing with the broader implications of a shifting global trade environment. The imposition of tariffs led to changes in production strategies, pricing models, and market positioning, as tech companies sought to manage both the direct financial impact and the longer-term uncertainties of an evolving trade relationship with China.
In this blog post, we will explore how Trump's tariffs have reshaped the US tech industry, with a particular focus on two key players: Apple and Nvidia. Through a detailed examination of their respective responses to tariff-related challenges, we will analyze the economic and strategic adjustments that have been made and assess the broader implications for the US tech industry in the context of global trade. We will also explore the economic, geopolitical, and long-term consequences of these policies, using data-driven insights to provide a comprehensive understanding of the shifts taking place in the tech world.
This examination aims to shed light on how these two industry giants have adapted to the pressures of an increasingly volatile trade environment. As the global trade war continues to evolve, understanding how major tech companies navigate these challenges will offer valuable insights into the future trajectory of the US tech sector and its role in the broader global economy.
Apple: Navigating Tariffs and Supply Chain Challenges
Apple, as one of the most prominent technology companies in the world, has been significantly affected by the tariffs imposed during the Trump administration. With a supply chain that spans across the globe, the company’s ability to maintain its production efficiency, profitability, and product pricing has been directly challenged by the introduction of tariffs on Chinese imports. Apple’s unique position, relying heavily on manufacturing and assembly in China, places it at the center of the discussion about the broader impacts of trade policy on the tech industry. This section will explore how tariffs have affected Apple’s supply chain, manufacturing strategies, pricing, and overall business operations.
The Impact on Apple’s Supply Chain and Manufacturing
Apple’s supply chain is deeply integrated with Chinese manufacturers, making it highly susceptible to the effects of the tariffs. A large portion of the company’s hardware components, such as semiconductors, display panels, and other critical parts, is sourced from Chinese suppliers. Additionally, the final assembly of Apple products, including the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook, occurs in China through its long-standing partnership with Foxconn and other manufacturing partners. The imposition of tariffs on these imports led to immediate cost increases for Apple, as components and assembly services from China became subject to additional duties.
The company faced an unprecedented challenge: to maintain its profit margins while dealing with the rising costs of these essential components. Given that Apple’s business model is centered around offering high-quality, premium-priced products, absorbing these additional costs was not a viable option without negatively impacting its pricing structure. Consequently, Apple had to make tough decisions regarding its supply chain and manufacturing operations, exploring ways to mitigate the effects of the tariffs while maintaining product quality and consumer demand.
One of the initial strategies Apple explored was to shift some of its manufacturing capacity out of China. In 2019, Apple began to move some of its production lines for the iPhone, along with other devices, to countries such as India, Vietnam, and other Southeast Asian nations. This move was aimed at reducing reliance on Chinese factories and mitigating the impact of the tariffs. However, shifting manufacturing to new regions is not a simple process. The company faced logistical challenges, such as adapting its supply chain to local conditions, establishing new relationships with suppliers, and ensuring that production capacity could meet the demand for Apple’s high-volume products.
Despite these efforts to diversify its supply chain, the challenge of maintaining quality control, consistency, and cost-effectiveness in new manufacturing locations remains significant. Many of Apple’s partners in these new regions were not as established as those in China, and the transition involved substantial investments in both time and resources to bring production capabilities up to the company’s high standards. Moreover, the ongoing trade war with China complicated Apple’s ability to execute these strategies swiftly, as geopolitical tensions continued to evolve.
Pricing and Consumer Demand
As tariffs increased the cost of components and assembly, Apple faced a difficult balancing act between protecting its profit margins and maintaining competitive pricing for consumers. The company’s premium products, which include the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook, have always been priced at a premium relative to competitors. This pricing strategy has been integral to Apple’s brand image, but with the added burden of tariffs, there was increased pressure to raise prices further or face a reduction in margins.
While Apple initially resisted price hikes, it eventually became apparent that absorbing the increased costs without passing them on to consumers would significantly impact profitability. For instance, in 2019, Apple raised the price of the iPhone in several markets due to increased manufacturing costs linked to the tariffs. These price hikes were not universally accepted and sparked concerns about the potential erosion of demand. Consumers, particularly in price-sensitive markets, began to question the value proposition of Apple products, especially when cheaper alternatives from competitors like Samsung, Huawei, and Xiaomi became more attractive.
Interestingly, Apple’s ability to maintain demand despite these price hikes can be attributed to its strong brand loyalty and the premium positioning of its products. However, the company has also made adjustments to its pricing strategies, particularly in emerging markets, where price sensitivity is higher. To offset the impact of the tariffs, Apple introduced new product models at lower price points, such as the iPhone SE, which allowed the company to cater to a broader range of consumers without sacrificing its brand image.
Diversifying Production and Strategic Adjustments
In addition to shifting some of its manufacturing capacity to other countries, Apple has increasingly turned to diversification as a strategy to hedge against the risks posed by the ongoing trade war. This diversification includes a broader approach to supplier sourcing and logistics, with an emphasis on reducing its reliance on Chinese-made components. For example, Apple has been working to increase the proportion of components sourced from countries outside of China, such as Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan.
Apple’s efforts to diversify its production also extended to its retail and sales operations. As tariffs affected product pricing and profitability, the company sought to expand its presence in markets outside of the United States and China, where the impact of tariffs was less pronounced. This included increasing its footprint in Europe and accelerating its market penetration in India, where the company had been pushing to expand its sales and manufacturing capabilities.
One of the key long-term strategies Apple has embraced is a move toward a more vertically integrated supply chain. This shift allows Apple greater control over its production processes, from component manufacturing to final assembly. The company’s push toward developing its own chips, such as the Apple M1 chip for its MacBook and iPad lines, is an example of this strategy. By reducing reliance on third-party suppliers, Apple can mitigate the risks associated with tariffs on imported components. This move also allows Apple to better control the pricing and availability of key parts, which is crucial in an environment characterized by supply chain disruptions.
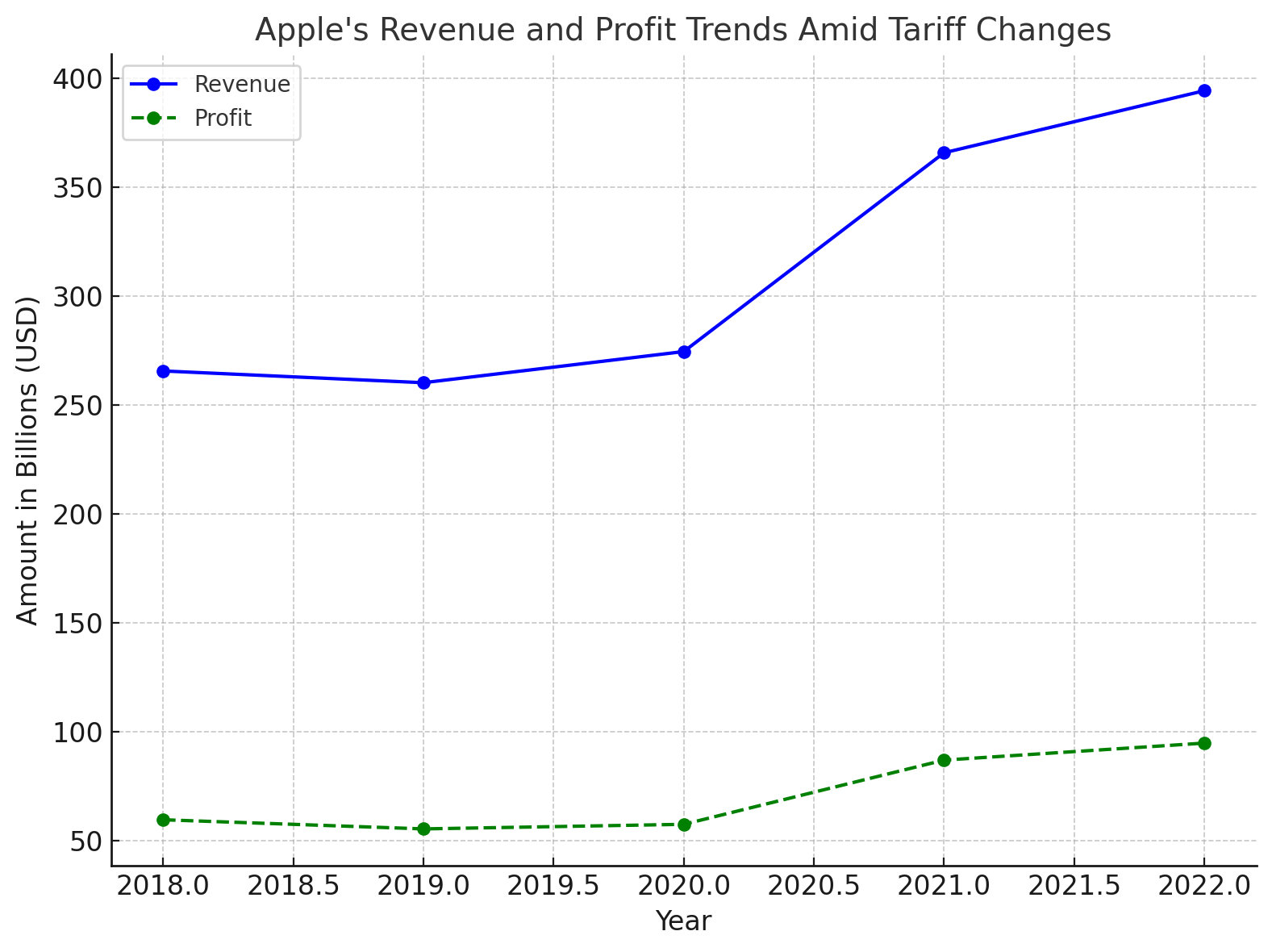
The financial performance of Apple, as illustrated in the accompanying chart, provides a clear picture of the company’s response to the challenges posed by the tariffs. While Apple has continued to see robust revenue growth, the impact of the trade war is reflected in the fluctuations in profit margins and regional sales performance. Notably, the company’s revenue from China saw a decline in certain quarters, while revenue from other markets, such as Europe and India, showed stronger growth. The chart underscores the company’s efforts to mitigate the impact of tariffs through pricing strategies and strategic diversification, which have allowed Apple to maintain a strong financial position despite external pressures.
Conclusion
Apple’s ability to navigate the challenges posed by the tariffs introduced during the Trump administration is a testament to its resilience and adaptability. While the company faced significant challenges in its supply chain, pricing, and market demand, its proactive approach to diversification, manufacturing shifts, and strategic adjustments have allowed it to weather the storm. However, the long-term implications of these trade policies remain uncertain. The company’s continued ability to adapt to changes in global trade relations and manufacturing landscapes will be crucial as it seeks to maintain its leadership position in the highly competitive tech industry.
As we move forward, it will be interesting to see how Apple continues to adjust its supply chain, pricing models, and strategic vision in response to the ever-changing landscape of international trade. The company’s experience serves as a valuable case study for other tech giants facing similar challenges, highlighting the importance of flexibility and innovation in navigating the complexities of a globalized market.
Nvidia: The Chipmaker's Response to Tariffs
Nvidia, a dominant player in the semiconductor industry, found itself uniquely impacted by the tariffs imposed during the Trump administration. As a leading producer of graphics processing units (GPUs) and other cutting-edge semiconductor technologies, Nvidia's business is highly reliant on international supply chains, especially in China, which plays a critical role in both manufacturing and market demand for its products. The imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports—particularly those related to high-tech components—had significant ramifications for Nvidia's operations. This section will explore the impact of these tariffs on Nvidia, how the company responded strategically, and what long-term adjustments have been made to navigate the shifting trade landscape.
The Impact on Nvidia’s Semiconductor Business
Nvidia’s core business revolves around the design and manufacture of semiconductors, with a particular focus on GPUs that power everything from gaming consoles to artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The company’s relationship with China is multifaceted: it not only sources critical components for its chips from Chinese manufacturers but also benefits from a large and growing market for its products within China. The tariffs imposed by the Trump administration were particularly detrimental to Nvidia because they increased the costs of manufacturing and the price of finished products. The additional duties on Chinese-made components, including semiconductors and circuit boards, translated into a substantial rise in Nvidia’s production costs.
One of the key components affected by these tariffs was the high-performance memory used in Nvidia’s GPUs. This memory is sourced from a limited number of suppliers, several of which are based in China. With tariffs on these imports increasing, Nvidia was forced to absorb additional costs, which affected its profit margins. Although the company could have passed these increased costs onto consumers, doing so would have risked making its products less competitive in the global market, especially in price-sensitive segments such as gaming.
The tariffs also affected Nvidia’s ability to access critical raw materials, such as rare earth metals, which are essential for semiconductor manufacturing. China is a dominant global supplier of these materials, and with tariffs driving up the cost of these materials, Nvidia’s production processes were directly impacted. This cost increase was compounded by global supply chain disruptions during the trade war, further straining the company’s ability to maintain consistent production timelines and cost-efficiency.
Nvidia’s Strategic Response to Tariffs
Given the high stakes, Nvidia was forced to adopt several strategic measures to mitigate the impact of the tariffs and maintain its competitive edge. The company’s first response was to explore alternative sourcing strategies to reduce its reliance on Chinese suppliers. Nvidia began working to diversify its supply chain, seeking out suppliers in other regions, such as Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan, to secure critical components at lower or more stable costs. This diversification strategy was designed to reduce the risk of future supply chain disruptions, especially if the trade war continued to escalate.
However, diversifying the supply chain was not an easy or quick fix. Nvidia faced several challenges in identifying suitable replacement suppliers capable of meeting the high-quality standards required for its cutting-edge products. In many cases, the companies Nvidia approached could not produce the volumes or precision necessary to meet the company’s demanding production requirements. Moreover, the transition to new suppliers often required a significant investment in R&D and logistical infrastructure, making it a time-consuming and costly process. Despite these obstacles, Nvidia’s efforts to secure a more diversified supply chain have allowed it to minimize the risks associated with its dependence on Chinese suppliers.
Another strategic response involved the company’s efforts to adjust its pricing models. Unlike Apple, which initially resisted price hikes, Nvidia took a more flexible approach to pricing, particularly for its high-end products. The company chose to absorb some of the additional costs in the short term, in order to maintain market share and avoid alienating consumers, especially in the highly competitive gaming and data center markets. However, as the trade war dragged on, Nvidia had to pass on some of these costs to customers, particularly for products that were heavily affected by tariff increases. This pricing adjustment was not without consequences. Nvidia faced some consumer pushback, especially in the gaming market, where customers are particularly sensitive to price increases.
In addition to pricing adjustments, Nvidia made a concerted effort to target new markets outside of China. While the Chinese market remains crucial for Nvidia’s growth, the company realized that its long-term success would depend on expanding its reach in other regions, particularly in the United States and Europe. Nvidia’s strategy to strengthen its presence in the cloud computing and artificial intelligence sectors became a central part of its long-term response to the tariffs. These industries, while still growing, are less dependent on Chinese demand and offer Nvidia an opportunity to diversify its revenue streams beyond the volatile gaming market.
Adaptations in Nvidia’s Research and Development Strategy
A critical element of Nvidia’s response to the trade war was its increased focus on innovation and technological development. The company’s investment in research and development (R&D) became even more important as it faced pressure from tariffs and increased competition from companies like AMD and Intel. Nvidia’s ability to stay ahead of the curve in terms of chip development and innovation would allow it to maintain its premium market position despite external pressures.
Nvidia’s push into AI and machine learning technologies provided an avenue to offset the impact of tariffs on traditional product lines. The company focused on expanding its portfolio of data center and AI-specific products, which are less susceptible to trade restrictions than consumer electronics like gaming GPUs. Nvidia’s acquisition of Mellanox Technologies in 2020 was a strategic move that enabled the company to broaden its presence in high-performance computing (HPC) and AI infrastructure, areas that are poised for significant growth regardless of tariff-related challenges.
Additionally, Nvidia’s development of the A100 Tensor Core GPU, designed specifically for AI and machine learning workloads, positioned the company as a leader in the rapidly expanding AI market. With AI becoming a key focus in both enterprise and consumer applications, Nvidia’s focus on innovation allowed it to secure new revenue streams that were less reliant on China and the gaming market.

To better illustrate Nvidia’s geographic focus and strategic shifts, the accompanying table provides a breakdown of the company’s market share in various regions before and after the implementation of tariffs. The table highlights how Nvidia’s focus on diversifying markets, particularly in the United States and Europe, has led to a shift in its revenue distribution. While the company’s market share in China has fluctuated due to tariff-related challenges, its expansion in other regions has allowed it to maintain its growth trajectory. This diversification strategy has been a key factor in mitigating the adverse effects of the trade war.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s response to the tariffs imposed during the Trump administration underscores the resilience and adaptability of the company in the face of significant geopolitical and economic challenges. Through diversification, pricing adjustments, and a focus on innovation, Nvidia has managed to navigate the pressures brought about by the trade war. However, the ongoing geopolitical uncertainty and evolving trade dynamics continue to pose risks for the semiconductor industry. Nvidia’s ability to sustain its growth and leadership in the tech industry will depend on its continued efforts to adapt to these changes and position itself at the forefront of emerging markets, such as artificial intelligence and high-performance computing.
The semiconductor industry, more than most others, is particularly vulnerable to the shifting tides of global trade policy. Nvidia’s experience serves as an example of how companies in this sector must not only respond to immediate challenges but also anticipate long-term disruptions in order to remain competitive. As trade relations evolve, Nvidia will likely continue to refine its strategies, balancing the need for cost-efficiency with the imperative to lead in technological innovation.
Economic and Geopolitical Implications for the US Tech Sector
The trade policies enacted during the Trump administration, particularly the imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports, have reverberated far beyond individual companies like Apple and Nvidia. The broader implications of these tariffs on the US tech sector are complex, extending well beyond the immediate impact on supply chains and pricing strategies. In this section, we will explore the economic and geopolitical consequences of Trump's tariff policies, examining their effects on the competitive dynamics within the tech industry, the US’s position in global markets, and the longer-term prospects for tech innovation and growth.
Economic Consequences of the Tariffs on the US Tech Industry
At the heart of the US tech sector’s response to the tariffs is the significant economic burden placed on companies reliant on global supply chains. US-based technology firms, many of which design and develop products domestically, depend on overseas manufacturing and sourcing for raw materials, components, and final assembly. The tariffs, which were often levied on Chinese imports, increased the cost of these essential inputs. This resulted in higher production costs for a range of tech products, including smartphones, laptops, and semiconductors.
For companies like Apple, Nvidia, and others in the sector, these increased costs were a significant challenge. While some companies, particularly in the consumer electronics space, were able to pass these costs onto consumers through price hikes, this was not always a viable strategy, especially in price-sensitive segments. For example, high-end products like Apple's flagship iPhones were affected, with higher tariffs potentially leading to a reduction in sales if prices were raised too much. On the other hand, companies operating in markets with thinner profit margins, such as those in the hardware space, faced more difficult decisions regarding whether to absorb these costs, adjust their product pricing, or seek cheaper alternatives to offset the tariff burdens.
The cumulative effect of these cost increases was a strain on the profitability of many tech companies, with some experiencing a reduction in earnings growth. As tech firms grappled with these challenges, they faced an additional concern: the global competitiveness of their products. As the tariffs increased production costs for US-based companies, it simultaneously provided an advantage to competitors from countries not subject to similar tariffs, particularly Chinese tech companies. This led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of US tech firms in global markets, where Chinese competitors like Huawei and Xiaomi could offer similar products at lower prices due to less stringent trade restrictions.
Moreover, the tariffs prompted a reevaluation of the US tech sector's dependence on China. Many companies began to consider diversifying their manufacturing operations and reducing their exposure to Chinese suppliers. However, this was easier said than done. The logistical complexity of relocating supply chains, particularly in the short term, posed significant operational challenges. The need for companies to find new suppliers and production facilities outside of China led to increased costs and delays, which ultimately affected overall efficiency and profitability.
Geopolitical Shifts and Their Impact on US Tech Firms
In addition to the direct economic consequences of the tariffs, there were significant geopolitical ramifications for the US tech sector. The US-China trade war was not just an economic battle; it was also a political struggle that reshaped the global power dynamics. The intensification of trade hostilities between the US and China introduced an element of unpredictability to global markets, forcing tech companies to adjust to a rapidly changing geopolitical environment.
One of the most significant geopolitical impacts was the growing sense of uncertainty regarding the future of the US-China trade relationship. Companies like Apple and Nvidia, which had previously enjoyed relatively stable access to the Chinese market, now faced an unpredictable regulatory environment. China, in retaliation for the tariffs, implemented its own trade barriers on US tech products, most notably targeting high-tech goods such as semiconductors, which had a direct impact on Nvidia. The Chinese government’s efforts to promote domestic alternatives to US tech products, particularly in the fields of semiconductors and telecommunications, also posed a significant threat to US tech companies.
Nvidia, for example, faced direct challenges in maintaining its position in China, as the country ramped up its investment in domestic semiconductor companies like SMIC (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation). These companies were able to produce some of the same types of chips as Nvidia, leading to increased competition in what had previously been a market largely dominated by US firms. For Apple, the growing geopolitical tensions meant that the Chinese government could potentially use its influence to reduce the market share of foreign companies, such as Apple, in favor of local brands like Huawei, which were less susceptible to the political forces at play.
Furthermore, the geopolitical uncertainty created by the US-China trade war forced many US tech firms to reconsider their supply chain dependencies. Companies were not only concerned about tariffs but also about potential government intervention, such as restrictions on technology exports or forced technology transfers. The imposition of such restrictions could hinder the ability of US companies to operate effectively in China, one of the world’s largest markets for technology products.
To address these concerns, many US-based tech companies began to adopt more diversified global strategies. This included establishing additional manufacturing and R&D centers in regions less vulnerable to trade wars, such as Southeast Asia, Europe, and India. Additionally, companies sought to cultivate new markets outside of China, especially in regions such as India, where the growing demand for technology products presents an opportunity to offset some of the challenges in the Chinese market.
Shifts in US Tech Leadership and Innovation
One of the more long-term impacts of the tariffs and the broader trade conflict has been a shift in the global leadership of technology innovation. Historically, the United States has been the undisputed leader in technological innovation, with Silicon Valley at the forefront of global tech development. However, as China has increasingly invested in its own technological capabilities, particularly in AI, semiconductors, and telecommunications, the balance of technological power has begun to shift.
China’s government has made strategic investments in its own tech companies, creating an environment in which companies like Huawei, Tencent, and Alibaba could thrive, even in the face of US tariffs. Moreover, China’s focus on becoming self-sufficient in semiconductor manufacturing—despite the challenges posed by the US trade restrictions—has enabled it to reduce its reliance on US-made chips. This has the potential to weaken the global dominance of US tech companies, as China’s increasing capabilities in fields like AI and 5G threaten to rival US technological advancements.
In response, US tech companies have ramped up their own investment in R&D and innovation to maintain their competitive edge. However, the tariffs have introduced significant barriers to collaboration and knowledge exchange between the US and China, particularly in fields where cooperation could have led to breakthroughs in areas like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 5G technology. The loss of access to China’s vast talent pool and market potential could result in slower growth for US companies in these emerging technologies.
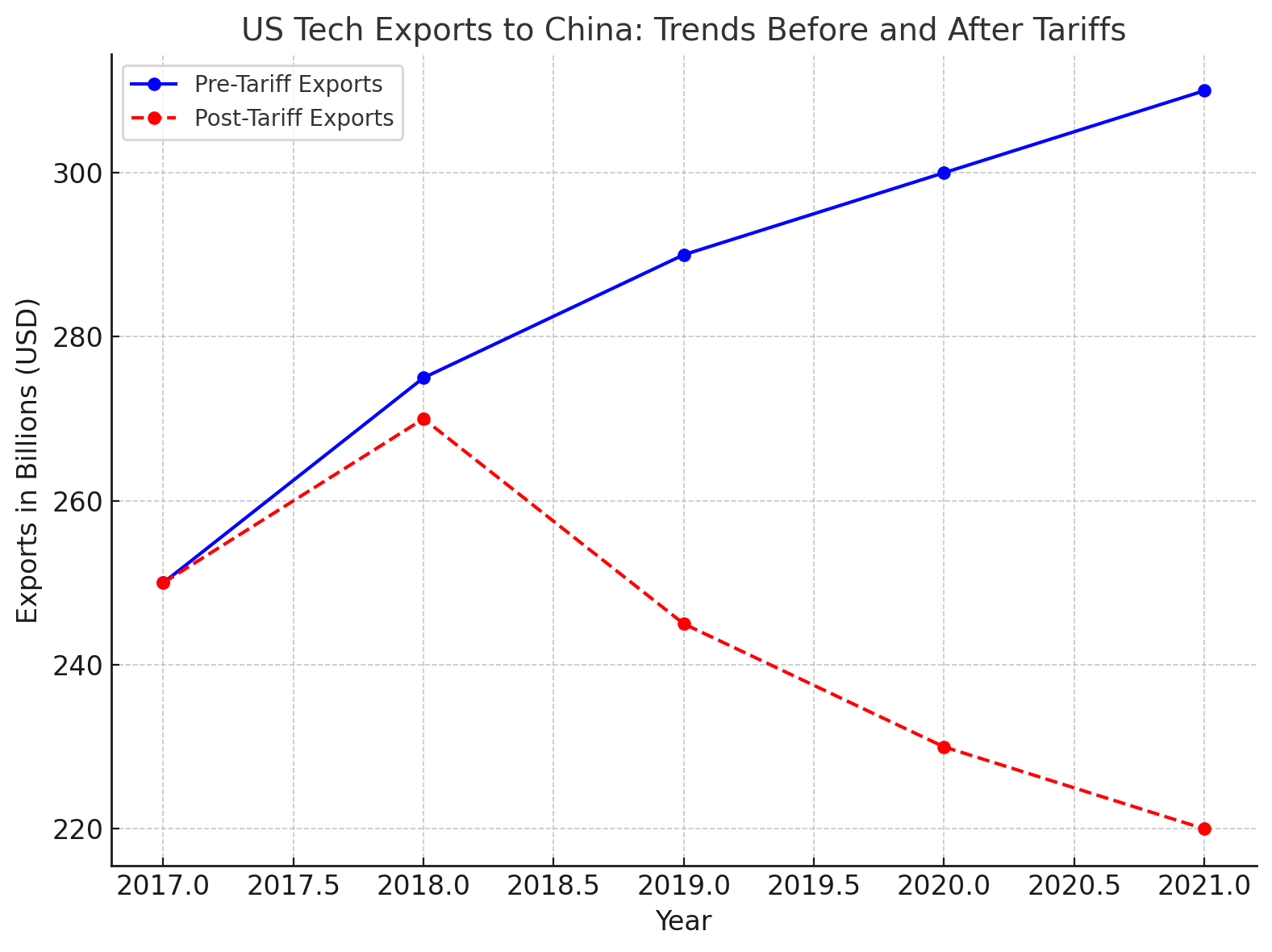
To further illustrate the economic and geopolitical impacts of the tariffs, the accompanying chart displays trends in US tech exports to China before and after the tariffs were implemented. The chart highlights a significant decline in US tech exports to China following the imposition of tariffs, which reflects the combined effects of trade barriers and shifting market dynamics. This decline underscores the direct impact of the trade war on the US tech industry’s ability to maintain its market share in China.
Conclusion
The economic and geopolitical implications of Trump’s tariff policies have had profound effects on the US tech sector. Companies like Apple, Nvidia, and others have had to navigate a challenging landscape characterized by rising costs, supply chain disruptions, and shifting global competition. The long-term impacts of these policies will continue to shape the competitive dynamics of the global tech market, with US companies facing increasing pressure from domestic rivals in China and other regions.
As the US tech sector moves forward, it must adapt to a more fragmented and unpredictable global landscape. Companies will need to diversify their supply chains, seek new markets, and invest heavily in innovation to maintain their competitive edge. While the trade war with China may have waned in intensity, its effects on the US tech industry are far from over, and the sector must remain agile in order to thrive in an increasingly multipolar world.
Looking Ahead – Navigating the Future of Tariffs and Tech
The implementation of tariffs under the Trump administration marked a significant turning point for the US tech industry. The ripple effects of these policies have been felt across the entire sector, as companies like Apple, Nvidia, and many others have had to reassess their supply chains, manufacturing strategies, and pricing models. The challenges posed by the tariffs have not only tested the resilience of US tech firms but also prompted a fundamental reevaluation of global trade dynamics and their impact on innovation. As we move forward, the question remains: How will US tech companies navigate the future of tariffs and an increasingly complex global market?
The Ongoing Impact of Tariffs on Tech Innovation
The immediate economic effects of the tariffs were starkly evident in the form of increased production costs, higher consumer prices, and disrupted supply chains. However, the longer-term impact is more nuanced, particularly regarding innovation. The US tech industry, which has long been a leader in global technological development, faces increased competition from countries like China, which is actively investing in its own technological infrastructure and capabilities. The tariffs have exacerbated this competition, as US tech companies now face a dual challenge: dealing with the costs of tariffs while also fending off growing domestic alternatives from China.
For companies like Nvidia, which is a leader in semiconductors, the stakes are especially high. The trade restrictions on semiconductors have opened the door for Chinese companies, such as SMIC, to gain market share in areas that were once dominated by US firms. In response, US companies must continue to innovate, not only in the development of new technologies but also in how they deliver these technologies to the global market. The ability to maintain a competitive edge in sectors such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing will be crucial for the survival and growth of US tech giants in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Moreover, the tariffs have led to a shift in how tech companies think about innovation. With the rise of trade tensions, there is now a stronger emphasis on self-sufficiency and reducing dependence on foreign supply chains. This has led to increased investments in domestic manufacturing capabilities and greater efforts to secure access to critical raw materials, such as rare earth elements. While this push toward self-reliance is a response to geopolitical pressures, it also presents an opportunity for the US tech industry to innovate in new areas, particularly in sustainable and high-tech manufacturing processes.
The Geopolitical Landscape: A New Era of Global Competition
The geopolitical ramifications of the US-China trade war, while initially seen as a short-term disruption, have evolved into a more profound transformation of global tech dynamics. As China continues to invest heavily in its tech sector, it is increasingly positioning itself as a global competitor to the United States. The tariffs imposed on Chinese products by the Trump administration served as a catalyst for China’s push to develop its own indigenous capabilities in sectors like semiconductors, telecommunications, and artificial intelligence. As a result, US tech companies must now contend with not only the direct effects of tariffs but also the broader challenge of competing with Chinese firms that are rapidly catching up in both innovation and scale.
In the short term, the tariffs created friction between the US and China, leading to a reduction in cross-border collaboration and trade in tech. However, as both countries continue to prioritize technological advancement, there is potential for the future development of new, more cooperative frameworks for global trade in technology. The evolving geopolitical environment could usher in new opportunities for US companies to engage in collaborations with other countries, particularly in emerging markets where technology adoption is accelerating.
One possible outcome of this geopolitical shift is the continued fragmentation of global tech markets. US-based companies, historically dominant in markets like North America and Europe, may find themselves needing to navigate a more diversified landscape. Markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Africa are expected to play an increasingly important role in the global tech ecosystem. US companies must adapt to these emerging markets, which present both opportunities for growth and new competition from regional players. This shift in focus could be pivotal for companies looking to sustain growth while mitigating the risks associated with tariffs and trade tensions in more traditional markets.
Navigating the Future: Key Strategies for US Tech Companies
As we look to the future, it is clear that the US tech industry must continue to adapt to the evolving global trade environment. The lessons learned from the tariff era will undoubtedly shape the strategies of tech companies moving forward. One key strategy will be diversification—not only in terms of supply chains but also in market access and product offerings. Companies like Apple and Nvidia are already making strides in diversifying their manufacturing operations, moving production to countries like India, Vietnam, and Mexico. By reducing their reliance on Chinese suppliers and manufacturing bases, they can better insulate themselves from future tariff-related disruptions.
Additionally, US tech companies must continue to innovate in order to maintain their competitive edge. While the rise of competitors in China poses a challenge, it also serves as a reminder of the importance of leading the charge in technological advancements. The US must continue to be at the forefront of emerging technologies such as AI, 5G, and quantum computing. These technologies are not only essential for the next phase of digital transformation but also provide opportunities for the US to assert its leadership in the global tech race. Companies that invest in R&D and push the boundaries of innovation will likely emerge as the key players in the next wave of tech disruption.
Another crucial strategy for navigating the future will be strengthening relationships with international partners. While the trade war between the US and China may have created divisions, the future may hold opportunities for new partnerships with countries outside of the traditional US-China axis. By forming alliances with other nations and regional blocs, US tech firms can secure access to new markets and resources, ensuring that they are well-positioned for success in an increasingly multipolar world.

To provide a clearer understanding of how the global competitive landscape is likely to evolve, the projected market shares for key tech sectors, such as AI, semiconductors, and telecommunications, are shown in the accompanying chart. The chart highlights the growing share of non-US companies in these areas, with China and other regions expanding their foothold. This data underscores the importance for US companies to remain agile and continue innovating in order to maintain their leadership in global tech markets.
Conclusion
The future of US tech companies in a post-tariff world is one filled with both challenges and opportunities. The tariffs imposed during the Trump administration served as a catalyst for significant change in how US tech companies operate, both domestically and internationally. As companies navigate this new global landscape, they must continue to adapt to shifting geopolitical and economic forces. Diversification, innovation, and strategic partnerships will be key to maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly evolving tech ecosystem.
While the legacy of tariffs will likely continue to shape the industry for years to come, the US tech sector has demonstrated its ability to adapt and thrive in the face of adversity. The next phase of growth for US tech companies will depend on their ability to leverage emerging markets, push the boundaries of technological innovation, and navigate the increasingly complex web of global trade and geopolitical relations. By embracing these strategies, US companies can not only weather future disruptions but also secure their place at the forefront of global technological leadership.
References
- "How US Tariffs Are Impacting the Tech Industry" - https://www.techradar.com
- "The Future of Tech in a Post-Tariff World" - https://www.forbes.com
- "Apple’s Supply Chain: Navigating Global Challenges" - https://www.cnbc.com
- "Nvidia’s Strategic Shift Amid Trade Tensions" - https://www.businessinsider.com
- "Global Trade and Tech: The Geopolitical Reality" - https://www.wsj.com
- "The US-China Trade War: Impacts on Technology and Innovation" - https://www.bbc.com
- "Rising Tariffs and Their Effect on Global Semiconductor Markets" - https://www.nytimes.com
- "Tech Giants Adapt to Tariffs: Apple, Nvidia, and More" - https://www.theverge.com
- "The Impact of Tariffs on US-China Tech Relations" - https://www.bloomberg.com
- "Navigating Global Trade for the Future of Tech" - https://www.reuters.com
