Nvidia vs Huawei: The Battle for AI Chip Dominance and the Future of Artificial Intelligence Hardware

The landscape of the AI chip market has long been dominated by a few key players, with Nvidia emerging as the undisputed leader in the field. Nvidia’s success has been largely attributed to its pioneering role in developing graphics processing units (GPUs) that cater to the high-performance needs of artificial intelligence (AI) workloads. With its robust software ecosystem, including CUDA and the deep learning platform, Nvidia has not only revolutionized gaming and graphics but also become an essential player in AI research, deep learning, and autonomous technologies. This near-monopoly has allowed Nvidia to build a commanding presence, especially in data centers, cloud computing, and AI-driven industries.
However, the advent of Huawei into the AI chip market marks a significant shift in the competitive dynamics. As a major player in telecommunications, Huawei has long been a formidable force in the global tech sector. The company, traditionally known for its telecom equipment and smartphones, is now making bold moves into the AI chip space, creating ripples of concern among established competitors. Huawei’s challenge to Nvidia is not merely a competition of products, but also an ideological battle that spans geopolitical concerns, market strategies, and future technological developments.
Huawei’s entry into the AI chip market is not just a reaction to Nvidia’s dominance but a well-calculated maneuver to reshape the future of AI hardware. With the rise of artificial intelligence as a transformative technology in industries ranging from healthcare to finance, cloud computing, and beyond, the demand for powerful AI chips has never been higher. Huawei is keen on capitalizing on this opportunity by leveraging its existing technological expertise, resources, and state-backed initiatives to challenge Nvidia’s supremacy.
As this competition unfolds, it will have far-reaching implications for the AI industry. The battle between these two tech giants will determine not only which company will dominate the AI hardware sector but also how the global AI landscape will evolve. The outcome could impact everything from research and development cycles to the shaping of AI policy in different regions, especially considering the complex geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China. In this article, we will explore Huawei’s strategy, its technological innovations, and how it is positioning itself to disrupt Nvidia’s AI chip monopoly.
Huawei’s Strategy in AI Chip Development
Huawei's venture into the AI chip market represents a significant shift in its business strategy, as the company seeks to extend its technological influence beyond its traditional areas of strength, such as telecommunications and smartphones. To effectively challenge Nvidia’s dominance in AI hardware, Huawei has adopted a multi-pronged strategy that involves heavy investment in research and development (R&D), the development of purpose-built chips for specific AI applications, and strategic partnerships to bolster its presence in the global market. These initiatives are designed not only to challenge Nvidia’s leadership but also to position Huawei as a key player in the growing AI ecosystem.
Commitment to Research and Development (R&D)
A cornerstone of Huawei's strategy is its heavy investment in R&D, which is fundamental to its ambition of creating competitive AI chips. According to company reports, Huawei has been allocating significant resources to research in AI, semiconductors, and machine learning. This focus has allowed the company to develop chips that are optimized for AI workloads, with an emphasis on high performance and energy efficiency.
Huawei’s in-house semiconductor division, HiSilicon, has played a pivotal role in the company’s AI chip development efforts. HiSilicon has leveraged its expertise in designing system-on-chip (SoC) products to create chips that are tailored to the unique demands of AI applications. The most notable product in this lineup is the Ascend series, a family of AI-focused chips that are designed to address the performance requirements of machine learning, deep learning, and data processing tasks. These chips are aimed at a variety of industries, including telecommunications, cloud computing, and automotive, offering a versatile solution for a wide array of AI use cases.
The Ascend 910, for instance, is a flagship AI processor that Huawei claims delivers significant improvements in computing power compared to its competitors. The chip is designed to provide both high performance and efficiency, with a special focus on enhancing AI processing tasks in large-scale data centers. With these investments, Huawei is positioning itself to compete directly with Nvidia’s top-performing GPUs, which are currently the go-to hardware for many AI and machine learning applications.
Development of Custom AI Chips for Specific Applications
In addition to the Ascend series, Huawei has also pursued the development of specialized AI chips designed to address the unique needs of specific industries and applications. For example, Huawei’s Kirin chipset series is primarily known for its integration into smartphones, but it has evolved over time to incorporate more powerful AI capabilities. The Kirin 990, for example, includes a dedicated NPU (Neural Processing Unit), which is designed to accelerate AI tasks such as facial recognition, object detection, and language processing on mobile devices. This type of specialization not only enhances the user experience but also demonstrates Huawei's ability to develop AI chips that are purpose-built for specific environments.
Huawei’s approach to developing custom chips for distinct markets is in direct contrast to Nvidia’s more generalized GPU offerings, which are often adapted for various use cases. By focusing on niche applications, Huawei is able to optimize its chips for performance in areas that Nvidia may not prioritize. This strategy is especially significant in regions where Huawei has strong relationships and a built-in customer base, such as China and other parts of Asia, where demand for AI solutions tailored to local industries is on the rise.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Huawei's strategy also involves forging strategic partnerships and collaborations with other companies, research institutions, and governments to enhance its position in the global AI chip market. These collaborations not only facilitate the adoption of Huawei's chips in a variety of sectors but also provide access to the necessary expertise and resources needed to further advance AI technologies.
One of the most notable partnerships is Huawei’s collaboration with China’s national research institutions, which has enabled the company to develop AI chips that are specifically tailored to the needs of the Chinese market. Huawei’s close ties with the Chinese government have allowed it to secure significant funding for its semiconductor R&D, which has proven essential for its competitive edge in the AI chip race. Furthermore, Huawei’s focus on building local partnerships in Asia is designed to circumvent the challenges posed by international trade restrictions, particularly those stemming from U.S. sanctions.
On the global front, Huawei has also entered into collaborations with cloud service providers, enterprises, and academic institutions to further refine its AI chip offerings. These partnerships allow Huawei to test its chips in real-world AI applications, such as autonomous driving, robotics, and data center management. By working with top-tier players in these industries, Huawei can continually improve the performance of its AI chips and make sure that they are competitive with those of Nvidia and other rivals.
Overcoming Geopolitical Challenges
Perhaps the most significant challenge facing Huawei in its quest to become a global leader in AI chips is the complex geopolitical environment in which it operates. The ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions and the imposition of sanctions on Huawei by the U.S. government have made it increasingly difficult for the company to access critical technologies, such as advanced semiconductors and software tools, which are essential for manufacturing AI chips. Despite these obstacles, Huawei has continued to innovate and find alternative solutions to maintain its chip production capacity.
One of the ways Huawei has addressed this issue is by ramping up its efforts to develop domestic alternatives to Western technologies. For example, the company has invested heavily in its own semiconductor fabrication capabilities, reducing its reliance on foreign chipmakers. Huawei has also sought to develop software ecosystems that can work seamlessly with its AI chips, including the MindSpore AI framework, which is designed to optimize AI model training and deployment on Huawei hardware.
By mitigating the impact of geopolitical tensions through innovation and self-reliance, Huawei is ensuring that its AI chips remain competitive, even in the face of external challenges. While it remains to be seen whether Huawei can overcome these geopolitical hurdles entirely, the company’s resolve to continue its AI chip development suggests that it is preparing to play a long-term game in the AI space.
Looking Ahead: Huawei’s Growing Influence in the AI Chip Market
Huawei’s AI chip strategy is already beginning to show signs of success. With its focus on high-performance chips, specialized products for specific industries, and strategic collaborations, Huawei is positioning itself to be a serious contender in the AI chip market. While Nvidia currently holds a commanding lead, the rapidly evolving AI landscape presents a window of opportunity for Huawei to make significant inroads.
As AI adoption continues to grow across sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and telecommunications, the demand for advanced, purpose-built AI chips will increase. Huawei’s strategic investments and partnerships place it in a strong position to capitalize on this trend, and its ability to innovate in the face of geopolitical challenges will determine its success in the years to come.
In conclusion, Huawei’s strategy in AI chip development is one that combines technological innovation, market specialization, and geopolitical savvy. By focusing on high-performance, purpose-built AI chips and cultivating partnerships that span industries and nations, Huawei is challenging Nvidia’s market dominance and signaling its intent to be a major player in the future of artificial intelligence.
Nvidia’s Market Leadership and Responses to Competition
Nvidia has long been the undisputed leader in the AI chip market, with its Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) forming the backbone of the AI revolution. While Nvidia originally gained fame for its dominance in the gaming industry, its strategic pivot toward AI and high-performance computing (HPC) over the past decade has solidified its place as the go-to provider for AI workloads. As a result, Nvidia has not only transformed how artificial intelligence is performed in data centers but has also redefined the role of GPUs in industries ranging from healthcare to automotive and cloud computing. However, as companies like Huawei begin to challenge its position, Nvidia must navigate a rapidly changing landscape, balancing innovation with a proactive response to emerging competition.
Nvidia’s Stronghold in the AI Chip Market
Nvidia’s rise to dominance in the AI chip market is rooted in the company’s ability to design GPUs that are optimized for parallel processing. Unlike traditional Central Processing Units (CPUs), which are designed for single-threaded tasks, GPUs are capable of handling thousands of simultaneous threads, making them ideally suited for the computationally intensive demands of machine learning and deep learning algorithms. This architecture has made Nvidia’s GPUs indispensable in modern AI research, especially in the training of deep neural networks (DNNs), where vast amounts of data must be processed in parallel.
The company’s flagship products, such as the A100 and H100 Tensor Core GPUs, are widely recognized as the gold standard for AI and machine learning tasks. These chips are designed to accelerate large-scale computations, making them a preferred choice in AI applications such as natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and autonomous vehicles. Nvidia’s CUDA programming model, which allows developers to write software that takes full advantage of GPU capabilities, further cements its leadership in the AI ecosystem by providing a robust software framework that complements its hardware.
Additionally, Nvidia’s investments in AI-specific hardware, such as the DGX systems, which combine powerful GPUs with high-bandwidth networking, have made it a leader in the high-performance computing (HPC) space. These systems are used by research institutions, universities, and enterprises worldwide, positioning Nvidia as the backbone of many AI innovations. The company’s ecosystem, comprising hardware, software, and support tools, has made it nearly impossible for competitors to match the performance and ease of use Nvidia provides to AI practitioners.
Dominance in AI Software Ecosystems
Beyond hardware, Nvidia’s dominance in the AI space is also driven by its software ecosystem. The company has strategically developed several key software solutions that optimize its hardware for AI tasks, making it an integrated offering for enterprises and researchers. One of Nvidia’s most significant software products is CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture), which enables developers to harness the full power of Nvidia GPUs for scientific computing, AI, and data analysis. CUDA has become the de facto standard for high-performance parallel computing, with a large community of developers and researchers using it to accelerate machine learning algorithms.
Another vital element of Nvidia’s software ecosystem is its NVIDIA AI Enterprise suite, which provides a set of tools and frameworks specifically tailored to the needs of businesses adopting AI at scale. This software stack ensures seamless integration with Nvidia’s GPUs, simplifying deployment and management for AI applications in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Additionally, Nvidia’s AI models, such as NVIDIA Clara for healthcare, NVIDIA Drive for autonomous vehicles, and NVIDIA Omniverse for 3D simulation and collaboration, have positioned the company as a key enabler in specialized fields. By providing pre-trained models, development platforms, and extensive support resources, Nvidia empowers companies to quickly develop and deploy AI applications across a wide array of industries, further reinforcing its leadership.
Nvidia’s Response to Huawei’s Challenge
As Huawei continues to develop competitive AI chips, Nvidia has responded with several strategic initiatives to maintain its leadership position. Recognizing the growing interest in custom, application-specific AI chips, Nvidia has accelerated the development of specialized hardware tailored to particular industries and use cases. For instance, Nvidia has launched chips optimized for AI workloads in automotive applications, such as the NVIDIA DRIVE Orin platform, which is designed to power autonomous vehicles with AI and deep learning capabilities. These specialized offerings allow Nvidia to continue its dominance in sectors where Huawei has not yet gained traction.
In addition to product diversification, Nvidia has also invested heavily in expanding its presence in the Chinese market, despite the growing geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China. Nvidia’s strategy in China has focused on offering localized solutions for AI research, leveraging the region’s growing demand for AI-driven applications, particularly in areas such as telecommunications, healthcare, and finance. While Huawei's chips are well-positioned to dominate within China, Nvidia’s established relationships with Chinese enterprises and research institutions give it a competitive edge in the region.
On the software side, Nvidia continues to strengthen its AI ecosystem with initiatives like NVIDIA Riva (an AI speech recognition framework) and NVIDIA Merlin (a recommendation systems framework), which help to enhance AI capabilities in a range of industries. These offerings reflect Nvidia's strategy of providing end-to-end AI solutions that combine hardware with specialized software tools to accelerate the development and deployment of AI technologies.
Nvidia has also doubled down on its efforts to stay ahead of the curve in deep learning and high-performance computing. With advancements such as the NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchip, which combines the computing power of the Grace CPU and the Hopper GPU architecture, Nvidia is positioning itself to lead the next wave of AI research in data-intensive fields like drug discovery and climate modeling.
Geopolitical Tensions and Strategic Partnerships
The current geopolitical environment, especially with the U.S. and China at odds, plays a significant role in Nvidia’s strategy. In response to the escalating U.S.-China trade tensions, Nvidia has sought to diversify its supply chain and reduce its reliance on Chinese manufacturers. The company has also taken steps to navigate the regulatory landscape by engaging in discussions with policymakers in both the U.S. and China, aiming to ensure that its products can continue to be sold in these markets.
Despite the challenges posed by Huawei’s domestic support and its ambitions to dominate the Chinese market, Nvidia has maintained strong relationships with key international players, including cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These partnerships are vital for Nvidia’s strategy, as they ensure widespread adoption of Nvidia’s GPUs for AI workloads in global data centers. By aligning with these cloud giants, Nvidia not only strengthens its market position but also ensures its hardware remains essential for enterprises and researchers across the globe.
Moreover, Nvidia’s recent acquisition of Arm Holdings, a leading semiconductor design company, has the potential to revolutionize the AI chip market. The acquisition could enable Nvidia to expand its product portfolio by offering custom chips designed specifically for the AI and IoT markets. This strategic move is designed to provide Nvidia with a broader range of chip architectures, allowing the company to compete more effectively with Huawei and other emerging competitors.
The Future of Nvidia in the AI Chip Market
While Huawei’s emergence as a competitor in the AI chip market is significant, Nvidia’s leadership in both hardware and software remains formidable. The company’s ability to innovate and adapt to new AI trends, along with its robust partnerships and established market presence, provides it with a strong foundation for maintaining its dominance. Moreover, Nvidia’s diversification into areas such as autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and edge computing presents new growth opportunities beyond traditional AI applications.
Nevertheless, the competition from Huawei, especially in the Chinese market, is likely to intensify in the coming years. Nvidia will need to continue refining its product offerings and expand its presence in emerging markets to fend off Huawei’s challenge. As the AI chip market continues to evolve, the rivalry between these two giants will be a defining feature of the next phase of technological advancement in AI.
Comparing the AI Chips
Technical and Market Differences
The battle between Huawei and Nvidia in the AI chip market is not just a contest of market presence but one rooted in significant technical and strategic differences. As both companies vie for dominance, the divergence in their approaches to chip design, technology optimization, and market positioning has profound implications for the industries and use cases that each can effectively serve. In this section, we will explore the technical and market differences between Huawei’s and Nvidia’s AI chips, providing a detailed comparison of their capabilities, architecture, performance, and strategic targets.
Technical Differences: Architecture and Design
The technical differences between Huawei’s and Nvidia’s AI chips stem from the companies' unique approaches to hardware architecture. While both companies aim to provide high-performance chips for AI workloads, they utilize distinct design philosophies suited to different sets of requirements.
Nvidia’s GPU Architecture
Nvidia’s GPUs have long been the gold standard for AI and machine learning applications, particularly due to their ability to process parallel workloads efficiently. The core strength of Nvidia’s architecture lies in its ability to handle high throughput and parallel processing. Unlike traditional CPUs, which are optimized for sequential task execution, Nvidia’s GPUs are designed to execute multiple tasks simultaneously. This makes them ideal for deep learning, where large datasets need to be processed in parallel.
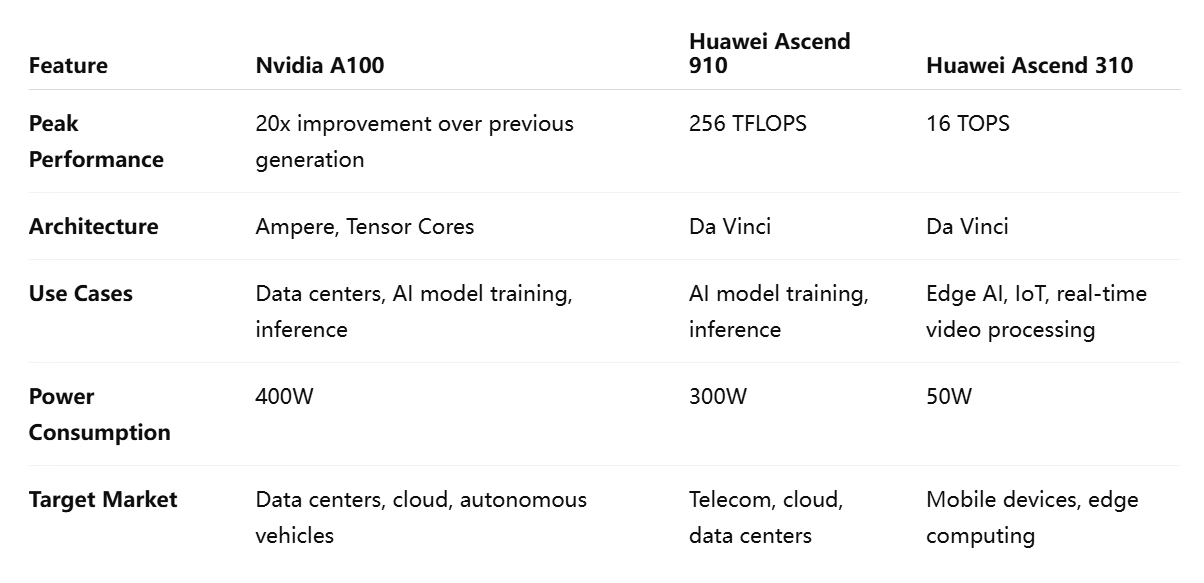
Nvidia’s Ampere architecture, used in its A100 and H100 GPUs, is particularly designed for AI and high-performance computing (HPC). The architecture integrates Tensor Cores, which accelerate deep learning operations and matrix multiplications, crucial for tasks such as training neural networks. The use of CUDA cores, along with a highly optimized software stack, allows developers to achieve maximum performance from Nvidia’s GPUs.
Huawei’s Ascend and Kirin Architectures
In contrast to Nvidia’s GPU-centered approach, Huawei’s focus is on creating specialized processors for AI tasks that go beyond traditional graphics processing. Huawei’s Ascend series, designed for AI inference and training, and its Kirin series for mobile applications both have distinct architectures optimized for the respective markets they target.
The Ascend 910, a flagship AI processor from Huawei, is built on the Da Vinci architecture, which Huawei claims delivers significant advantages in both power efficiency and processing performance. Unlike Nvidia’s GPUs, which are optimized for general-purpose AI workloads, the Ascend 910 is designed specifically for AI training, using parallel processing to accelerate tasks in data centers. Huawei’s Ascend 310, designed for edge computing, emphasizes low power consumption, making it ideal for deployment in areas with constrained energy resources such as mobile networks and IoT devices.
The Kirin 990 chipset, Huawei’s flagship mobile chip, integrates an NPU (Neural Processing Unit), allowing it to accelerate AI tasks directly on the device. Unlike Nvidia’s GPUs, which require external systems for deployment, the Kirin series enables on-device AI processing, reducing latency and reliance on cloud infrastructure. This chip’s integration of AI processing within smartphones is a critical differentiator in the mobile sector, where Nvidia’s GPUs are typically not used.
Performance Comparison
When comparing the performance of Huawei’s and Nvidia’s AI chips, it’s essential to consider several metrics, including processing speed, energy efficiency, and scalability.
Nvidia’s Performance in AI Workloads
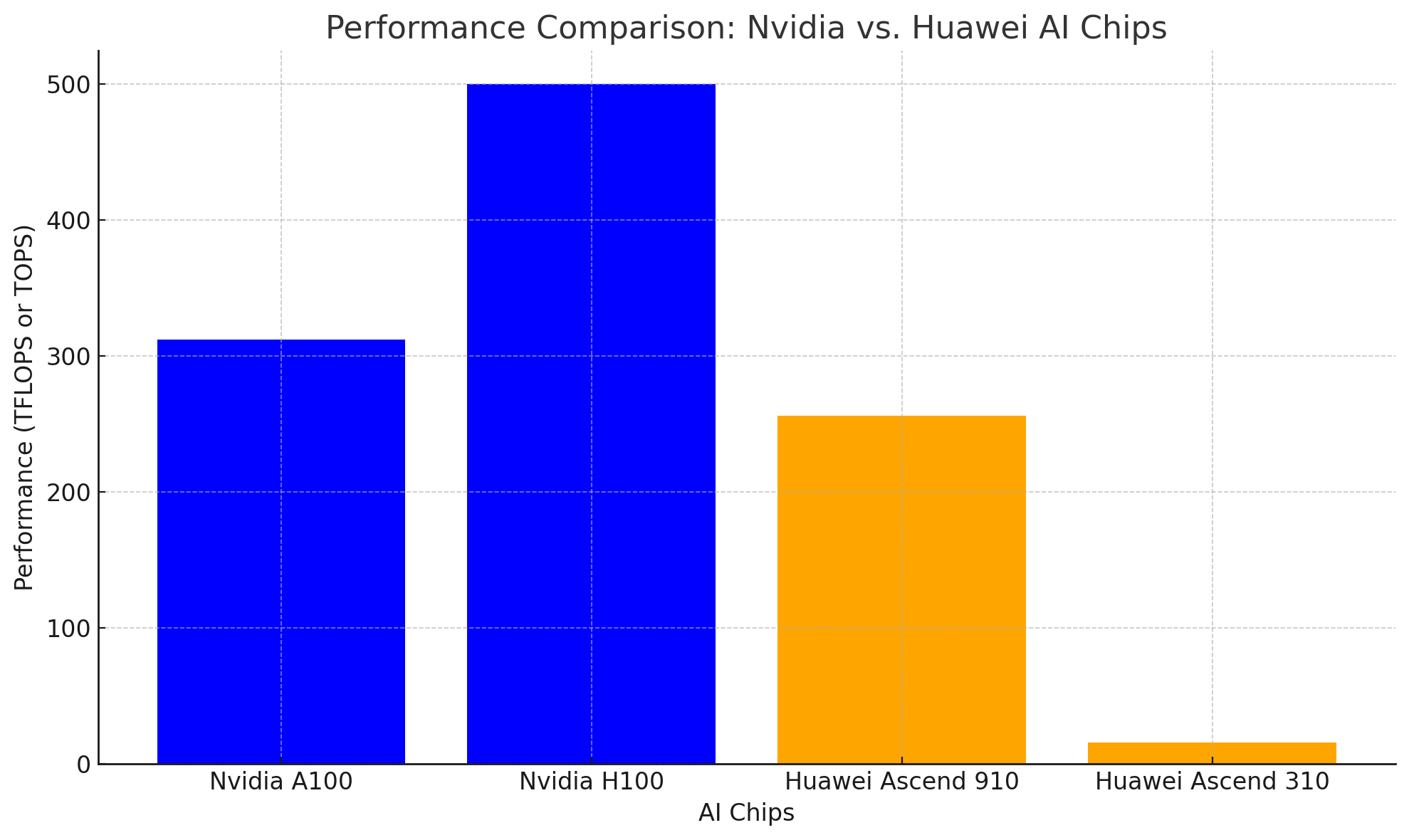
Nvidia’s GPUs have consistently outperformed competitors in AI tasks, thanks to their design for parallel processing and optimization for AI model training. The A100 Tensor Core GPU, built on the Ampere architecture, offers unmatched performance for deep learning workloads, with capabilities reaching up to 20 times the speed of its predecessor, the V100, in certain AI applications. The A100’s ability to scale in cloud and enterprise environments, as well as its robust support for both AI training and inference, has made it a preferred choice for large-scale AI model development, particularly in data centers.
Furthermore, Nvidia’s DGX systems, which combine multiple A100 or H100 GPUs, enable enterprises to build powerful AI supercomputers. These systems are optimized for multi-GPU performance, which further enhances their appeal for training sophisticated AI models. The integration of Nvidia’s NVIDIA NVLink high-bandwidth interconnect technology allows GPUs to work in tandem with minimal bottlenecks, enhancing overall computational efficiency.
Huawei’s Performance in AI Applications
Huawei’s Ascend 910 processor claims to deliver peak performance of up to 256 teraflops (TFLOPS) in AI processing, which positions it as a direct competitor to Nvidia’s A100 in terms of raw computational power. Huawei emphasizes the chip’s efficiency, particularly in edge computing and AI inference tasks, where its optimized design can execute AI models at a lower power consumption than Nvidia’s GPUs. In these areas, Huawei’s chips are tailored to serve applications where energy efficiency is paramount, such as in mobile devices, smart cameras, and autonomous vehicles.
The Ascend 310 chip, while not as powerful as the Ascend 910, is designed for deployment in environments where power consumption and space are limited. It offers up to 16 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) and is built for edge AI processing, where low latency is crucial. This chip is most often used in edge AI applications, such as real-time video processing and IoT devices, where Huawei’s low-power, high-efficiency model outshines Nvidia’s high-performance but energy-hungry GPUs.
Market Differences: Target Sectors and Adoption
Nvidia’s Market Leadership and Diverse Adoption
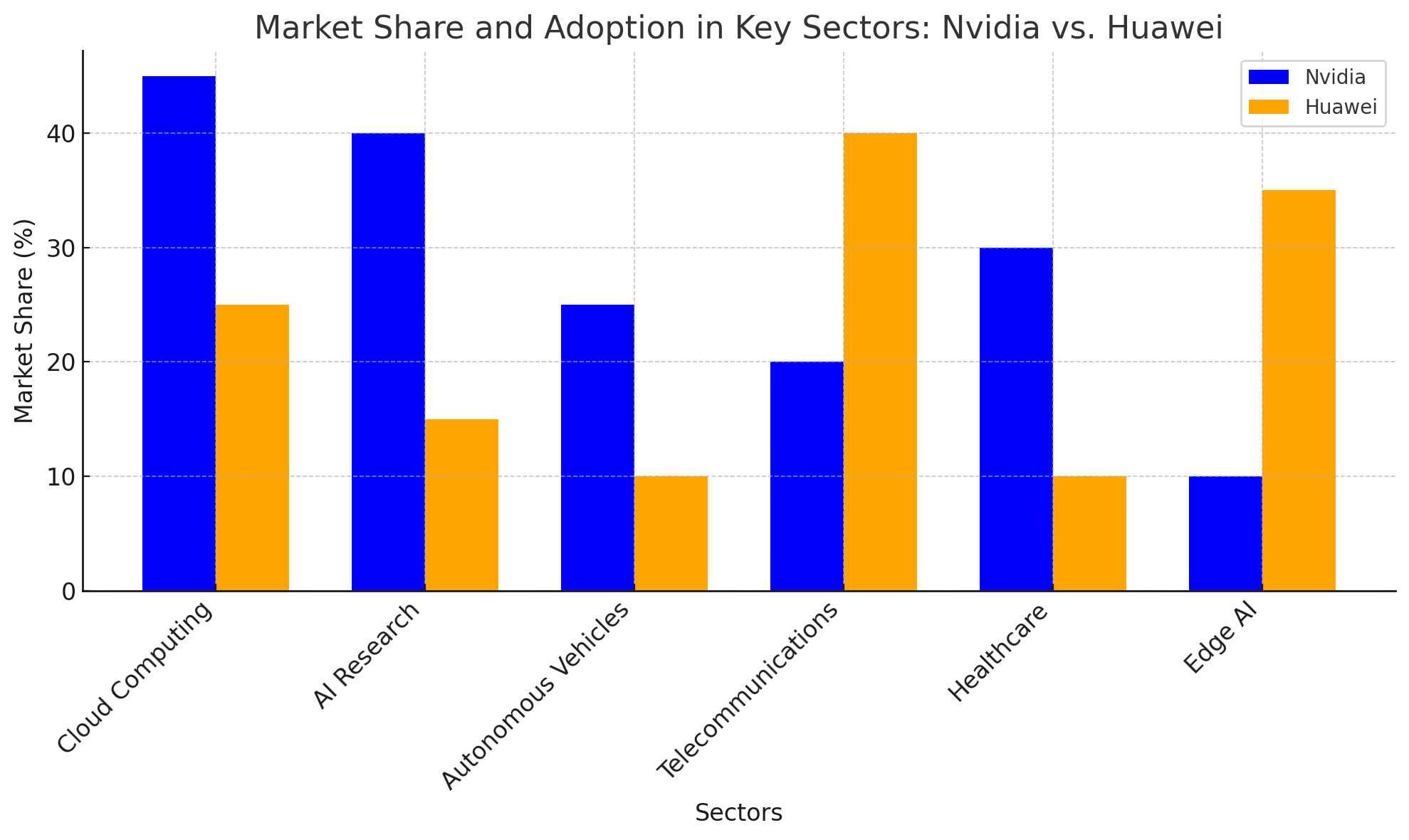
Nvidia’s AI chips are widely adopted across several high-growth industries, including data centers, cloud computing, autonomous vehicles, gaming, and healthcare. Nvidia has established itself as a leader in AI and machine learning, with its products dominating the research and development efforts of major AI labs and research institutions. For instance, Nvidia’s GPUs are heavily used in autonomous vehicle development, where they power deep learning algorithms for object detection, decision-making, and path planning.
In the enterprise sector, Nvidia’s products are integral to cloud computing platforms, where companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud use Nvidia GPUs to accelerate AI and machine learning services. This widespread adoption across industries has allowed Nvidia to maintain a dominant position in the AI chip market.
Huawei’s Focus on Telecommunications and the Chinese Market
Huawei’s AI chip strategy is distinctly focused on certain sectors, particularly telecommunications, mobile devices, and edge computing. Huawei’s chips, such as the Ascend 310, are integral to its 5G and IoT solutions, offering the computational power necessary to support the massive amounts of data generated by these technologies. Huawei’s Ascend processors are heavily used in telecom infrastructure, where they power AI-based features such as network optimization and predictive maintenance.
Huawei also focuses on the Chinese market, where its products enjoy significant support due to the company’s close ties with the Chinese government and its leadership in telecommunications. Despite facing challenges in Western markets due to geopolitical tensions, Huawei’s strong domestic base provides a significant advantage, especially in regions where Nvidia is less entrenched.
Key Differences in Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are crucial factors in determining which chip can best serve large-scale AI applications. Nvidia’s DGX systems and support for multi-GPU configurations offer unparalleled scalability for large enterprise clients looking to scale their AI infrastructure quickly. Nvidia has designed its GPUs to work seamlessly in both on-premise data centers and in cloud environments, making it highly adaptable to different deployment models.
Huawei, on the other hand, focuses on a more diversified approach. While its Ascend 910 can handle large-scale AI workloads, the company’s emphasis on edge computing and mobile AI means that Huawei’s chips are often deployed in smaller, more distributed environments. This gives Huawei an edge in sectors that require real-time, localized AI processing, such as smart cities, healthcare IoT, and autonomous vehicles.
Key Specifications and Benchmarks
Who Will Lead the AI Chip Market
As the AI chip market continues to grow at an unprecedented rate, the competition between Huawei and Nvidia is set to define the future landscape of artificial intelligence hardware. Both companies are investing heavily in R&D and strategic partnerships, with each aiming to secure a dominant position in the rapidly expanding market. However, the outcome of this competition will depend not only on technological innovation but also on geopolitical factors, market adoption, and the ability to adapt to evolving AI trends. In this section, we will explore the potential future trajectories of both companies and assess which of the two is better positioned to lead the AI chip market in the years to come.
Nvidia’s Position: Strengths, Opportunities, and Challenges
Nvidia has firmly established itself as the leader in the AI chip market, thanks to its dominant position in both hardware and software. The company’s GPUs, such as the A100 and H100, have become the standard for AI researchers and enterprises alike, thanks to their performance, scalability, and versatility. Nvidia’s strategy of integrating hardware and software into an optimized AI ecosystem, with products like CUDA and NVIDIA AI Enterprise, has given it a significant edge over its competitors, making it an integral part of AI development across a wide range of industries, from healthcare to autonomous vehicles.
Looking ahead, Nvidia is well-positioned to maintain its market leadership due to several factors. Firstly, its CUDA platform, which is widely adopted by AI researchers and developers, continues to grow in importance. The widespread usage of CUDA ensures that Nvidia’s GPUs will remain the default choice for many AI applications, particularly those involving deep learning. Moreover, Nvidia’s recent innovations, such as the Grace Hopper Superchip, which combines CPU and GPU architecture into a unified solution, highlight its commitment to pushing the boundaries of AI chip performance and efficiency.
Additionally, Nvidia’s deepening relationships with major cloud service providers, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, place it in an advantageous position in the growing AI-as-a-Service market. These partnerships ensure that Nvidia’s chips will continue to be integral to large-scale AI deployments, especially as enterprises increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure to power their AI workloads.
However, Nvidia faces several challenges that could impede its ability to maintain its dominant position. The first and most significant challenge is the growing competition from companies like Huawei. As Huawei continues to develop its own AI chips and expand its market presence, particularly in China, Nvidia could face increased pressure in certain sectors, particularly in regions where Huawei has a strong foothold. Furthermore, the ongoing geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China could complicate Nvidia’s ability to access the Chinese market, which is vital for its future growth.
Another potential threat to Nvidia’s leadership is the rise of custom AI chips developed by other tech giants. Companies like Google and Amazon, which already design custom chips for their cloud services (such as Google’s TPU and Amazon’s Inferentia), may also intensify competition in the AI chip space. If these companies continue to scale their AI chip production, Nvidia may lose some of its market share in certain applications, particularly in cloud-based AI.
Huawei’s Position: Strategic Initiatives and Market Expansion
Huawei’s entry into the AI chip market is relatively recent, but the company’s strong backing from the Chinese government, as well as its expertise in telecommunications and semiconductor manufacturing, has allowed it to make significant strides. Huawei’s Ascend series of AI chips, particularly the Ascend 910 and Ascend 310, are positioned as direct competitors to Nvidia’s offerings, with a focus on high performance and energy efficiency. Additionally, Huawei’s deep integration of AI into its 5G infrastructure and IoT ecosystem has given its chips a unique edge in telecommunications, an area where Nvidia has less dominance.
One of Huawei’s key advantages lies in its domestic market, where it enjoys significant government support and widespread adoption of its products. The Chinese government’s emphasis on developing a self-sufficient semiconductor industry has enabled Huawei to secure substantial investments in AI chip development. This support has allowed Huawei to rapidly scale its production capacity and establish itself as a leading provider of AI chips within China and other parts of Asia. Huawei is particularly well-positioned to benefit from the growing demand for AI chips in sectors such as telecommunications, smart cities, and edge computing.
In addition to its domestic success, Huawei is working to expand its footprint in global markets. Despite facing challenges in the U.S. and Europe due to political and security concerns, Huawei’s AI chips are gaining traction in markets like the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia. Huawei’s focus on AI for edge computing, where low power consumption and real-time processing are essential, positions it as a strong player in the rapidly growing IoT and 5G sectors. The company’s ability to tailor its products for these markets, where Nvidia’s GPUs are less commonly deployed, provides it with a competitive edge.
However, Huawei’s path to global leadership is not without its challenges. The ongoing trade restrictions imposed by the U.S. have severely impacted Huawei’s ability to access critical technologies, such as advanced semiconductor fabrication equipment and AI software. These restrictions have slowed down the company’s ability to scale its production of advanced AI chips, which could limit its long-term growth prospects. Furthermore, Huawei’s reliance on the Chinese market could be a double-edged sword, as it leaves the company vulnerable to geopolitical shifts and trade disputes.
Market Trends and the Growing Importance of AI Chip Innovation
As the AI chip market continues to evolve, there are several key trends that will shape the future of this industry. One of the most important trends is the shift towards specialized AI chips designed for specific use cases. While general-purpose GPUs like Nvidia’s A100 and H100 will continue to play a critical role in AI research and development, the growing demand for edge AI and IoT solutions is driving the need for custom chips optimized for low power consumption and real-time processing. Huawei’s Ascend 310 chip, which is optimized for edge AI applications, exemplifies this shift towards specialized hardware.
The rise of AI-as-a-Service platforms, which allow enterprises to offload AI workloads to cloud providers, will also impact the AI chip market. As more companies turn to the cloud to access AI tools, the competition between Nvidia, Huawei, and other chip manufacturers will intensify. Nvidia’s strong presence in cloud computing, coupled with its strategic partnerships with major providers, gives it an edge in this area, but Huawei’s focus on 5G and edge computing could help it capture a significant portion of the market.
Another important factor to consider is the growing importance of sustainability in AI chip development. As AI workloads become more resource-intensive, there is increasing pressure on chipmakers to develop more energy-efficient solutions. Nvidia’s focus on energy-efficient GPUs, such as those used in the A100, aligns with this trend. However, Huawei’s emphasis on power-efficient chips, such as the Ascend 310, positions it as a strong contender in the push for more sustainable AI hardware.
The Future of AI Chip Leadership
While Nvidia remains the current leader in the AI chip market, its future dominance is not guaranteed. The rise of competitors like Huawei, with its strong domestic market and specialization in edge computing and 5G, presents a formidable challenge to Nvidia’s global supremacy. Nvidia’s ability to maintain its leadership will depend on its continued innovation in AI hardware, its ability to adapt to emerging market trends, and its ability to navigate the geopolitical landscape.
On the other hand, Huawei’s growth prospects are closely tied to its ability to overcome geopolitical hurdles and expand its presence in global markets. If Huawei can continue to innovate and scale its AI chip production, particularly in edge computing and 5G, it could challenge Nvidia’s leadership in the coming years. However, the company’s reliance on the Chinese market and the challenges posed by trade restrictions will continue to impact its ability to compete at a global scale.
In conclusion, the future of the AI chip market is still uncertain, with both Nvidia and Huawei vying for dominance. The outcome of this competition will likely be determined by a combination of technological innovation, market adoption, and the ability to navigate complex geopolitical dynamics. As AI continues to evolve, the companies that can stay ahead of the curve in developing specialized, efficient, and scalable AI chips will ultimately determine the future of the industry.
References
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2020/06/10/how-nvidia-is-driving-the-ai-revolution/
- https://www.huawei.com/en/technology/ai
- https://www.theverge.com/2021/3/15/22331416/nvidia-arm-acquisition-ai-chips-competition
- https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-56343594
- https://www.techradar.com/news/why-huawei-looks-to-take-on-nvidia-in-the-ai-chip-market
- https://www.cnbc.com/2022/01/25/nvidia-report-highlights-ai-dominance-in-silicon-market.html
- https://www.zdnet.com/article/why-huawei-ai-chipset-strategy-will-challenge-nvidia-in-5g/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/22/huawei-ai-chip-ascend-910-launch.html
- https://www.theinformation.com/articles/huawei-challenges-nvidia-with-next-generation-ai-chip
- https://www.wired.com/story/huawei-ai-chip-design-future/
