Baidu’s Resurgence Amidst AI Competition

In a surprising turn of events, Baidu Inc., one of China's leading internet and artificial intelligence (AI) companies, has reported a notable revenue increase in the first quarter of 2025, defying broader market expectations and shifting investor sentiment. Once overshadowed by domestic competitors and burdened by decelerating advertising revenues, Baidu’s latest financial performance underscores a significant transformation underway within the firm—its decisive pivot toward AI and cloud computing. As the Chinese tech sector navigates through a complex and intensely competitive AI arms race, Baidu’s resurgence not only reaffirms its long-standing technological capabilities but also signals a broader reconfiguration in China’s digital economy.
Founded in 2000 as a search engine company often referred to as "China’s Google," Baidu has gradually repositioned itself as a pioneer in the development of AI infrastructure, particularly through innovations in language models, autonomous driving systems, and cloud services. Despite facing fierce competition from Tencent, Alibaba, ByteDance, and other rising challengers, Baidu’s continued investment in generative AI technologies and scalable enterprise solutions is beginning to yield measurable returns. This recent financial uptick arrives at a critical moment, as the Chinese government intensifies its AI ambitions amid geopolitical tension, U.S. export restrictions, and internal market volatility.
The context in which Baidu’s Q1 earnings report emerges is both turbulent and transformative. Globally, tech companies are contending with the economic aftershocks of the pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating investor confidence. In China, these factors are compounded by ongoing regulatory overhauls and a strategic push for domestic innovation in advanced technologies, especially AI. Against this backdrop, Baidu's unexpected 3% year-over-year revenue growth—fueled largely by a 40% surge in non-advertising revenues from its AI cloud segment—presents a compelling narrative of resilience, reinvention, and technological leadership.
What makes Baidu’s performance particularly noteworthy is the company’s ability to offset a sustained decline in its traditional online marketing business. As consumer behavior shifts and regulatory measures restrict digital advertising practices, companies heavily reliant on ad revenue have struggled to maintain growth. Baidu, however, has countered this downward trend through strategic investment in ERNIE (Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration) large language models, the expansion of its Apollo autonomous driving platform, and an aggressive build-out of its AI-powered cloud infrastructure. These initiatives not only differentiate Baidu from its tech rivals but also align closely with China’s broader national agenda to lead in AI innovation by 2030.
Moreover, Baidu’s open-sourcing of its ERNIE models and the ongoing refinement of ERNIE Bot versions—now up to ERNIE 4.5—demonstrate the company’s intent to attract a wider community of developers, researchers, and enterprise clients. By fostering openness in an increasingly fragmented AI ecosystem, Baidu seeks to cement its foundational role in shaping the next generation of AI applications. The company’s integration of generative AI across multiple service layers, from consumer search tools to cloud APIs, reflects a multi-dimensional strategy designed to capture both public and enterprise value.
This blog post delves into the multi-faceted dimensions of Baidu’s recent financial revival and its implications for the company’s future prospects. It begins with a detailed breakdown of Baidu’s first-quarter performance, followed by an exploration of the strategic realignment that has enabled this resurgence. We then examine the competitive landscape of China's AI market, comparing Baidu’s positioning against rivals. Finally, the discussion culminates in a forward-looking analysis of the opportunities and challenges Baidu faces as it navigates a rapidly evolving global AI race.
In an industry where quarterly earnings often serve as leading indicators of strategic soundness, Baidu’s surprise revenue jump serves as more than a fleeting headline—it is a marker of the company's adaptability and renewed relevance. As China’s AI battle intensifies, Baidu appears not just to be participating but shaping the very future of digital intelligence in the world’s second-largest economy.
Financial Performance Breakdown
Baidu’s first-quarter 2025 earnings report offers a detailed and compelling view into the company’s evolving revenue composition, signaling a pivotal transformation from a search-driven advertising giant into a diversified technology powerhouse. The financial performance for the period ending March 31, 2025, surpassed market expectations on several fronts, reflecting not only internal efficiencies but also the traction of Baidu’s AI-powered business lines. While macroeconomic headwinds and regulatory tightening continue to exert downward pressure on traditional revenue channels, Baidu’s robust results in the AI cloud and enterprise services segment stand out as a primary growth engine.
Top-Line Growth and Earnings Surprises
The company reported total revenues of ¥32.45 billion (approximately $4.50 billion), representing a 3% year-over-year increase. While this figure may appear modest in isolation, it carries substantial weight given the broader slowdown in China’s digital advertising market. Analysts surveyed prior to the earnings release had forecasted a largely flat quarter or a minor contraction in revenue due to ongoing declines in ad spending and consumer sentiment. Baidu’s ability to outperform those expectations illustrates the effectiveness of its diversification strategy and operational adaptability.
Equally notable was Baidu’s adjusted net income, which rose to ¥7.01 billion ($970 million), marking a significant uptick compared to the prior year and exceeding consensus projections. This improvement was attributed to a combination of higher-margin AI-related services, tighter cost controls, and increased efficiencies across R&D and infrastructure. The company’s EBITDA margin also saw sequential improvement, indicating that revenue gains were not offset by proportionally higher expenses.
Segment-Wise Revenue Composition
Baidu’s business is primarily divided into two core revenue categories: online marketing and non-online marketing services. For Q1 2025, the company reported online marketing revenue of ¥17.31 billion, which marked a 6% year-over-year decline. This segment, traditionally the company’s cornerstone, continues to be adversely affected by declining advertiser budgets, stricter content regulations, and an evolving digital ecosystem where users are increasingly consuming content through closed-loop applications.
In contrast, Baidu’s non-online marketing revenue—principally composed of cloud services, intelligent transportation, and enterprise AI—rose to ¥9.4 billion, registering a staggering 40% year-over-year growth. This increase highlights the company’s shift away from an ad-centric model and its growing competence in monetizing artificial intelligence innovations across verticals.
A closer examination of the AI cloud business shows that Baidu is gaining ground in a highly competitive market. Its AI cloud now supports clients across manufacturing, transportation, and public services, offering solutions such as large language model integration, smart city platforms, and automated customer service agents. These enterprise-grade services are significantly more resilient to cyclical downturns and offer higher margins than consumer-facing advertising.
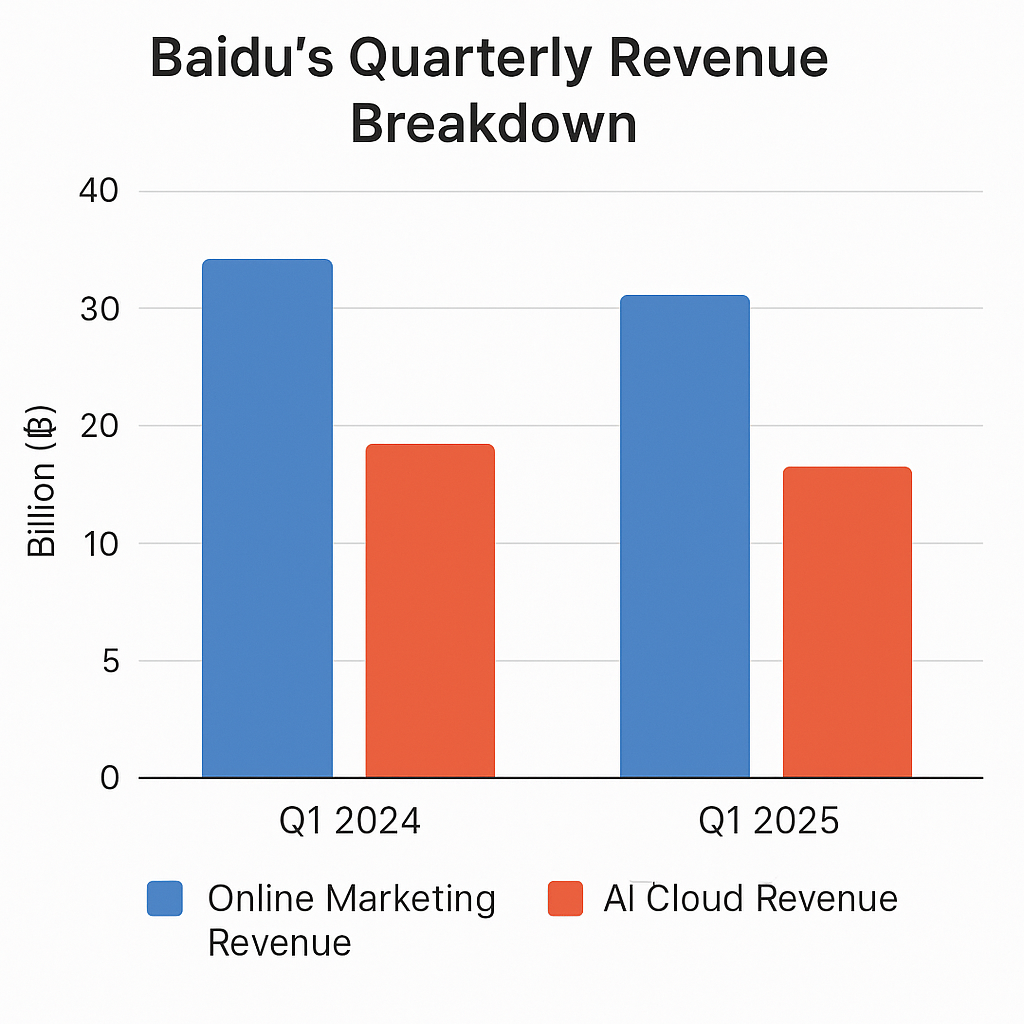
This revenue bifurcation paints a clear picture: Baidu’s growth is increasingly being driven by its ability to innovate and sell AI services rather than rely on digital ads. Such a transition is not only strategically sound in light of regulatory and economic pressures but also aligns with global shifts toward enterprise AI solutions.
Cost Structures and Profitability Dynamics
On the expense side, Baidu’s operational expenditures remained stable year-over-year, with notable efficiency improvements in its R&D division. While the company continues to invest heavily in the development of its ERNIE family of large language models and in its Apollo autonomous driving unit, management has implemented tighter financial discipline. These efforts have yielded lower overall R&D-to-revenue ratios without sacrificing technological innovation.
Additionally, Baidu’s general and administrative expenses as a share of total revenue declined slightly, indicating better cost governance. Marketing and promotional expenditures were also adjusted downward, which is consistent with the company’s strategic transition from user acquisition to enterprise client onboarding and retention.
Baidu’s balance sheet remains strong, with a healthy cash reserve and low debt levels. The company’s cash and short-term investments stood at ¥188 billion at the end of Q1, providing ample liquidity to support ongoing innovation, infrastructure expansion, and potential strategic acquisitions.
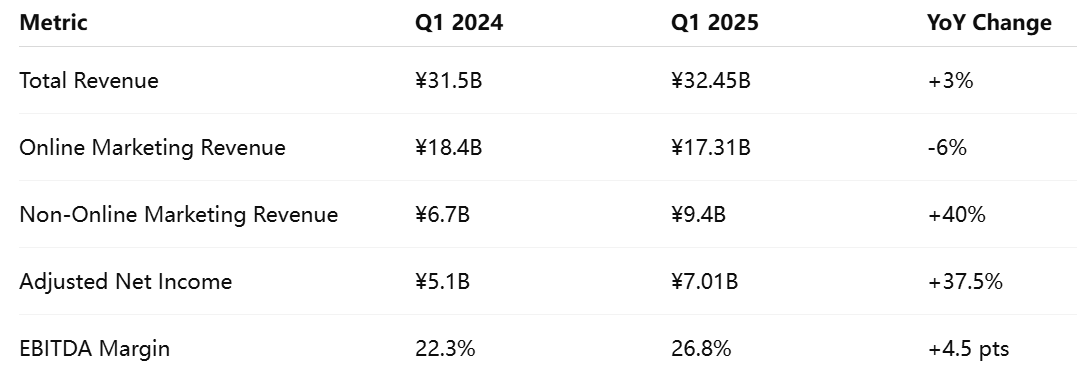
The table above consolidates Baidu’s core financial metrics, highlighting its strong earnings performance and the stark contrast in growth trajectories between its declining ad business and thriving AI cloud segment.
Investor and Market Reactions
Following the earnings release, Baidu’s U.S.-listed shares rose by nearly 7% in after-hours trading, reflecting renewed investor confidence in the company’s strategic direction. Market analysts from both domestic and international firms have subsequently upgraded their outlook on Baidu, citing its AI monetization potential and consistent execution as key factors.
Nevertheless, some cautioned that sustaining this growth trajectory would require continued investment in model optimization, expansion of the cloud ecosystem, and regulatory compliance—particularly in areas involving AI ethics and data governance.
In summary, Baidu’s financial performance in Q1 2025 underscores a pivotal inflection point in the company’s operational model. While online advertising may continue to decline, the firm’s strength in AI infrastructure, enterprise services, and cloud computing provides a sustainable and profitable path forward. The financial results serve not only as a quarterly success story but also as early evidence that Baidu's AI-first strategy is delivering material shareholder value.
Strategic Shift: Embracing AI and Cloud Services
Baidu’s recent financial performance is not merely a function of cost optimization or cyclical market dynamics—it is a clear byproduct of a fundamental transformation in the company’s strategic direction. Central to this transformation is Baidu’s focused pivot away from its long-standing reliance on digital advertising and toward the scalable potential of artificial intelligence and cloud services. In this section, we explore how Baidu has restructured its operations, deployed advanced AI models, and realigned its corporate identity to capitalize on China’s burgeoning AI economy.
From Search to Solutions: The AI-First Imperative
Baidu’s early success was anchored in its role as China’s dominant search engine. For nearly two decades, the company profited immensely from advertising revenue tied to its search platform and various content ecosystems. However, by the mid-2010s, emerging trends began to challenge this model. Mobile-first usage, walled gardens created by competitors, and tightening regulations around digital content compelled Baidu to diversify its value proposition. This culminated in a formal declaration of its “AI-first” strategy, signaling a profound organizational shift.
The commitment to this vision is most evident in the growth and prominence of Baidu AI Cloud, a division that now serves as the principal revenue driver outside of advertising. Baidu AI Cloud has matured into a full-stack platform offering intelligent computing, machine learning services, data analytics, and vertical-specific solutions to enterprises and public sector clients. The growth of this segment has been extraordinary: in Q1 2025 alone, non-online marketing revenue—driven primarily by AI cloud—surged 40% year-over-year to ¥9.4 billion. This pivot reflects not only successful execution but also growing market demand for AI-native enterprise capabilities.
ERNIE Models and the Rise of Generative AI
At the core of Baidu’s AI transformation lies its proprietary language model series, ERNIE (Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration). Since the launch of ERNIE 1.0 in 2019, Baidu has iteratively enhanced the model, culminating most recently in ERNIE 4.5 and the open-source ERNIE X1 framework. These models compete with global leaders like OpenAI’s GPT, Google’s Gemini, and Meta’s LLaMA. Baidu has emphasized efficiency and multilingual capability as competitive differentiators, positioning ERNIE as more accessible and cost-effective for both developers and enterprises.
ERNIE Bot, built atop the ERNIE model family, has seen rapid adoption across both B2B and B2C applications. In addition to integration within Baidu’s own search engine, the bot powers customer service solutions, intelligent document processing, and knowledge management systems. The company’s decision to open-source the ERNIE X1 model signals a broader commitment to ecosystem development—an approach aimed at encouraging third-party adoption and innovation.
This open-source move is particularly strategic given the geopolitical climate surrounding AI development. With increasing scrutiny over data sovereignty and model transparency, Chinese enterprises and institutions are under pressure to utilize domestically developed AI. By offering a robust open-source alternative, Baidu is aligning with state-backed efforts to reduce dependency on Western models while cultivating trust and extensibility within the Chinese developer community.
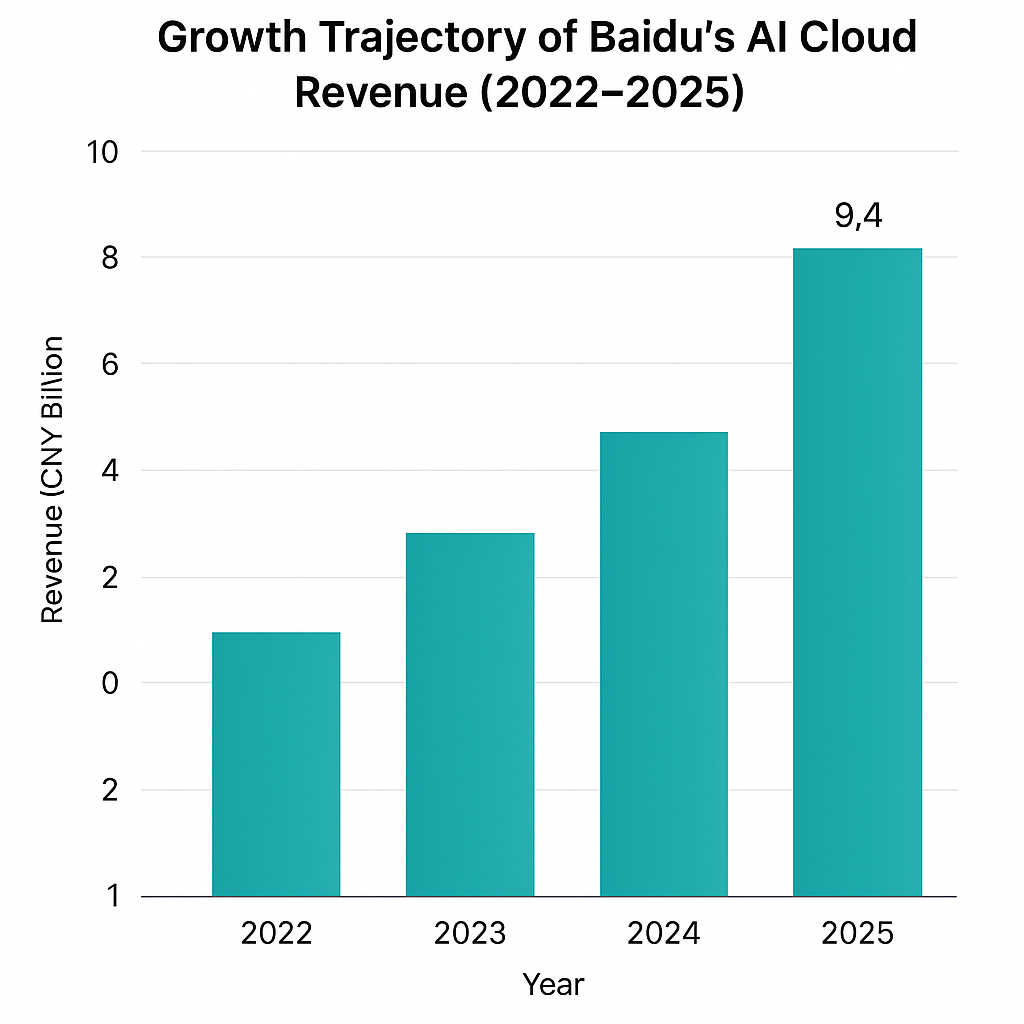
The continued scaling of Baidu AI Cloud is heavily reliant on the performance and flexibility of the ERNIE model family. As organizations in manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and government look to automate workflows and extract insights from large datasets, Baidu’s AI services are positioned to become indispensable. Furthermore, the company is integrating ERNIE into its suite of cloud APIs, creating a seamless interface for enterprise clients to leverage advanced NLP and vision capabilities with minimal friction.
Apollo, Smart Transportation, and Edge Intelligence
Beyond language models and cloud services, Baidu is also investing heavily in intelligent transportation systems through its Apollo division. This includes autonomous driving, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) infrastructure, and smart traffic management solutions. While the monetization of autonomous vehicles remains in its early stages, Baidu has made significant progress with its robotaxi services in cities like Wuhan, Chongqing, and Beijing. In Q1 2025, Apollo operated over 826,000 rides, cementing its status as a leader in commercialized autonomous transport within China.
In addition to its robotaxi initiative, Baidu’s contributions to smart city development have begun to yield tangible results. Its AI-powered traffic optimization systems, installed in multiple municipalities, help regulate congestion, reduce emissions, and improve safety. These systems feed into the broader national mandate to digitize infrastructure—a policy priority under China’s 14th Five-Year Plan. By embedding AI into physical environments, Baidu is not only expanding its revenue streams but also cementing its role as a national technology partner.
Edge AI, or the deployment of machine learning models on devices at the periphery of the network, is another frontier in Baidu’s strategy. This includes smart cameras, industrial sensors, and embedded automotive modules that can process data locally for real-time decision-making. Edge AI addresses key issues around latency, bandwidth, and data privacy—areas that are increasingly important for sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and public safety.
Strategic Benefits and Long-Term Viability
The diversification of Baidu’s AI portfolio offers both financial and strategic advantages. From a revenue standpoint, AI services tend to generate higher margins and longer customer lifecycles compared to digital advertising. More importantly, enterprise AI adoption is less susceptible to short-term consumer behavior or platform disruptions. As AI capabilities become embedded into core business processes, client retention and recurring revenue streams naturally increase.
Moreover, Baidu’s cross-sector capabilities allow it to bundle services and develop integrated solutions—a major selling point for Chinese enterprises seeking turnkey digital transformation. This capability not only improves competitiveness but also increases switching costs, thereby enhancing client stickiness.
From a policy alignment perspective, Baidu’s AI-first model dovetails neatly with national goals of technological self-reliance, data sovereignty, and industrial modernization. The company’s strategic roadmap echoes key objectives of government programs such as “New Infrastructure,” “Made in China 2025,” and “Next Generation AI Development Plan.” This congruence ensures regulatory goodwill and potential access to public contracts and funding opportunities.
Baidu’s strategic shift toward AI and cloud computing is no longer a speculative pivot—it is a well-executed transformation supported by both market validation and policy alignment. Through investments in foundational models, enterprise solutions, and intelligent infrastructure, Baidu is redefining itself for the AI era. As global competition intensifies and technology cycles accelerate, this proactive realignment will likely be the cornerstone of the company’s next decade of growth. Whether measured by financial performance, product innovation, or strategic positioning, Baidu has successfully positioned itself as a central player in China’s evolving AI ecosystem.
Navigating China’s Competitive AI Landscape
Baidu’s recent resurgence and strategic repositioning must be contextualized within the broader environment of China’s hypercompetitive artificial intelligence (AI) sector. Over the past decade, China has emerged as a global AI superpower, home to some of the world’s largest and most innovative technology companies. This emergence has been driven by both state policy and private enterprise, with firms like Tencent, Alibaba, Huawei, and ByteDance investing heavily in AI infrastructure, research, and application-layer services. Against this backdrop, Baidu’s ability to distinguish itself is both a strategic feat and a testament to its deep technological roots.
Mapping the Competitive Landscape
China’s AI ecosystem is characterized by rapid iteration, aggressive scaling, and intense rivalry. At the enterprise level, major technology firms are racing to build foundational models, cloud-native platforms, and vertically integrated AI services. These developments are taking place in parallel with national-level initiatives aimed at achieving AI self-reliance and global leadership.
Baidu’s key competitors include:
- Alibaba Cloud (Aliyun): A market leader in cloud computing, Alibaba has extended its dominance by integrating large language models (e.g., Tongyi Qianwen) into its enterprise SaaS products. It enjoys widespread adoption among e-commerce, logistics, and financial institutions due to its commercial versatility.
- Tencent Cloud and Hunyuan Model: Tencent is leveraging its ecosystem of social platforms, gaming, and financial services to deploy AI in diverse real-world scenarios. Its Hunyuan model is designed to support large-scale, multilingual tasks and is already embedded into WeChat’s ecosystem.
- Huawei Cloud and PanGu Models: Huawei’s emphasis on AI hardware-software co-optimization allows it to deliver end-to-end AI stacks. Its PanGu series of models supports a range of applications from medical imaging to industrial robotics, bolstered by its proprietary Ascend AI chips.
- ByteDance and its Self-Developed AI Stack: While best known for its consumer-facing platforms like TikTok (Douyin), ByteDance has rapidly scaled its internal AI capabilities. Its entry into enterprise AI with tools aimed at productivity, content generation, and data analysis signals growing ambition in the space.
Despite formidable competition, Baidu retains unique advantages. Unlike Alibaba or Tencent, whose AI strategies are interwoven with vast consumer and transactional data ecosystems, Baidu’s legacy in search and natural language processing (NLP) offers a deep foundation for developing high-performing large language models. Furthermore, its long-term investments in autonomous driving and smart transportation give it differentiated exposure to AI use cases beyond the cloud.
Regulatory Alignment and State Support
China’s AI policy is governed by a series of national initiatives, including the "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan" released by the State Council. This document outlines a roadmap for China to become the world’s primary AI innovation center by 2030. It emphasizes the development of homegrown foundational models, ethical AI frameworks, and strategic technologies such as chips, quantum computing, and edge AI.
Baidu’s trajectory aligns closely with these objectives. As an early recipient of government-backed funding for autonomous driving and as one of the first companies to receive approval for AI-powered search integration, Baidu enjoys favorable regulatory status. The company has participated in various state-led AI testing zones and collaborates with public sector agencies to deploy its smart city infrastructure solutions.
This alignment with national objectives provides Baidu with several strategic advantages. First, it ensures greater access to critical data and public-private partnership opportunities. Second, it insulates the company from some of the unpredictable regulatory swings that have impacted peers in adjacent industries. And third, it positions Baidu as a trusted technology vendor in government-led digital transformation initiatives.
That said, operating within China’s AI ecosystem is not without constraints. The country’s increasingly strict data privacy laws, content moderation rules, and algorithmic transparency requirements necessitate careful compliance. Moreover, the recent trend toward favoring open-source models and open innovation frameworks means that proprietary platforms must continually prove their value to developers and institutional clients alike.
Technology Differentiation in a Crowded Field
While the competition in China’s AI industry is formidable, Baidu’s continued emphasis on innovation and differentiation is evident. The ERNIE model family has been designed with a focus on knowledge-enhanced pre-training, enabling improved reasoning, inference, and domain-specific performance. Unlike some peers who rely on raw token prediction, Baidu incorporates structured knowledge bases into its models, improving accuracy in vertical use cases such as healthcare, education, and finance.
Additionally, Baidu is strategically developing multimodal models that integrate language, vision, and speech. These models are increasingly in demand across smart hardware, robotics, and autonomous driving applications—domains where Baidu has already established operational platforms through its Xiaodu and Apollo subsidiaries.
One area where Baidu stands out is its cross-silo integration of AI across infrastructure, model, application, and hardware layers. For instance, Baidu’s Kunlun AI chips power ERNIE inference workloads in its own cloud data centers, providing cost savings and control over compute availability—an essential advantage in an era of GPU scarcity and U.S. export restrictions. This vertical integration mirrors the approach of leading U.S. firms like Google and Amazon and positions Baidu to compete at a global scale.
Balancing Competitive Pressure and Market Opportunity
While Baidu’s positioning is strong, the company must continuously adapt to market dynamics. The commoditization of foundational models and the proliferation of open-source alternatives threaten to erode pricing power in AI cloud services. To mitigate this, Baidu has emphasized value-added services—such as fine-tuning, data annotation, and workflow integration—to maintain differentiation.
Moreover, customer expectations are evolving. Enterprises now demand not only high-performing models but also ethical AI practices, transparent governance structures, and explainability. Baidu has responded by releasing detailed documentation on ERNIE’s training corpus, implementing bias mitigation tools, and engaging with academic researchers to promote responsible AI.
The company also faces pressure from rapidly evolving regulatory frameworks. China’s Interim Measures for the Management of Generative AI Services, enacted in 2023, require model providers to ensure output accuracy, prevent misinformation, and register with relevant authorities. Baidu has proactively incorporated these requirements into its AI lifecycle, positioning itself as a compliant and stable partner in a space marked by regulatory flux.
Baidu’s ability to thrive in China’s fiercely competitive AI landscape is the result of deliberate strategic choices, technological excellence, and regulatory synchronization. Its continued focus on language models, enterprise AI, autonomous mobility, and cloud infrastructure provides a balanced and resilient foundation for long-term growth. As the AI race in China intensifies—with billions of dollars in investment and policy attention—Baidu has emerged as both a pioneer and a survivor. Navigating this complex environment demands not only innovation but also agility, compliance, and trustworthiness—all of which Baidu has begun to demonstrate with increasing consistency.
Baidu’s Path Forward
Baidu’s surprising revenue jump in the first quarter of 2025 is not merely a quarterly anomaly, but rather a culmination of years of strategic recalibration and technological foresight. As the company emerges from a period of structural transformation and competitive pressure, it stands as a symbol of adaptability in one of the world’s most aggressive AI battlegrounds. This conclusion draws together the key themes explored throughout the blog, framing Baidu’s recent performance as a leading indicator of its broader trajectory in China’s AI-driven digital future.
At a glance, Baidu’s Q1 earnings tell a compelling story of resilience. A 3% year-over-year revenue increase, achieved amid a shrinking online advertising market, reflects the company’s success in cultivating new, AI-centered revenue streams. More significantly, the 40% surge in non-online marketing revenues—driven primarily by Baidu’s AI cloud services—demonstrates that its pivot to enterprise-grade, generative AI solutions is not just viable but increasingly lucrative. In doing so, Baidu has made substantial progress in lessening its historical dependence on ad revenue, a transition that positions the company to endure future regulatory, competitive, or economic shocks.
Baidu’s transformation is underpinned by the continuous development of its ERNIE large language models and the expanding reach of its AI cloud ecosystem. The open-sourcing of ERNIE X1 and the rollout of ERNIE Bot 4.5 signal Baidu’s ambition to democratize AI development while maintaining performance parity with global benchmarks. This open architecture approach enables third-party developers, researchers, and enterprises to co-create value with Baidu, accelerating ecosystem growth and broadening adoption.
Furthermore, Baidu’s efforts are not confined to software alone. With its Kunlun AI chips, Apollo autonomous driving program, and intelligent transportation initiatives, the company is also building a vertically integrated AI infrastructure stack. This positions Baidu to serve both commercial and civic sectors, and aligns directly with China's national vision of achieving technological self-reliance in strategic industries.
What distinguishes Baidu in China’s crowded AI market is its ability to balance ambition with accountability. While competitors may have scale or consumer dominance, Baidu’s combination of advanced NLP, hardware-software integration, and enterprise focus gives it a multifaceted edge. Its long-term commitment to regulatory compliance, ethical AI, and open innovation adds a layer of stability that is increasingly attractive to institutional clients and government partners.
However, challenges remain. The competitive threat from Alibaba, Tencent, ByteDance, and Huawei will continue to intensify, particularly as these firms pursue their own advancements in foundational models and cross-sector AI applications. At the same time, global geopolitical tensions and U.S. export controls over semiconductors may constrain Baidu’s access to high-performance GPUs, impacting its training and deployment capacities. To mitigate these risks, Baidu must accelerate efforts to optimize its in-house Kunlun chips and explore alternate sources of compute efficiency, such as model quantization and federated learning frameworks.
Additionally, Baidu must scale its AI commercialization efforts across industries beyond technology—particularly in manufacturing, energy, retail, and finance. While its early wins in public sector partnerships and transportation are commendable, the next phase of growth will demand a deeper integration of AI into the everyday operations of China's industrial base. This will require more than technical sophistication; it will demand domain-specific customization, long-term support structures, and collaborative deployment models with end users.
On the global front, Baidu faces reputational and operational limitations due to its geographic concentration and perceived proximity to the Chinese government. To expand internationally, the company must establish credibility as a trusted, neutral AI provider. This could include compliance with international standards for data privacy, security certifications, and joint ventures with neutral third-party partners in markets like Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
Nonetheless, the core thesis remains optimistic. Baidu has achieved what many deemed improbable: a successful reinvention in the midst of a transformative and unforgiving technological cycle. The company’s financial outperformance, model innovation, and operational discipline are not isolated wins, but indicators of a scalable blueprint for long-term relevance. With the foundational elements now in place—robust models, regulatory alignment, cloud delivery infrastructure, and strong leadership—Baidu is poised to not only compete in China’s AI race but potentially define its contours.
As we look ahead, Baidu’s trajectory will serve as a critical case study in how legacy tech firms can evolve, thrive, and lead in the age of artificial intelligence. Whether it continues to outperform will depend on its ability to scale sustainably, innovate responsibly, and collaborate strategically. In an era where AI is reshaping the competitive logic of nearly every industry, Baidu’s journey is emblematic of the new industrial paradigm—where value is created not merely through software or hardware, but through intelligence itself.
References
- Baidu Investor Relations – Earnings Reports
https://ir.baidu.com/financials/quarterly-results - Reuters – Baidu Beats Revenue Estimates on AI Cloud Growth
https://www.reuters.com/technology/chinas-baidu-beats-revenue-estimates-ai-cloud-services-offset-ad-weakness - TechCrunch – Baidu’s AI Push Yields Financial Gains
https://techcrunch.com/2024/05/baidu-ai-cloud-growth-quarterly-earnings - SCMP – China's AI Titans Battle for Dominance
https://www.scmp.com/tech/big-tech/article/baidu-alibaba-tencent-ai-cloud - The Register – ERNIE Bot Evolves to Compete Globally
https://www.theregister.com/baidu-ernie-4-launch-generative-ai - Nikkei Asia – China's Baidu Launches Next-Gen LLM
https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Technology/China-Baidu-generative-AI-ERNIE - Bloomberg – Baidu Rides AI Wave to Beat Market Expectations
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/baidu-surpasses-forecasts-with-ai-cloud - CNBC – Chinese Tech Stocks Rebound on AI Earnings Optimism
https://www.cnbc.com/2024/05/baidu-shares-rise-ai-cloud-q1-report - MIT Technology Review – AI Regulation and China’s Strategic Goals
https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/05/china-ai-regulation-industry-impact - Harvard Business Review – Strategic Pivoting in AI Enterprises
https://hbr.org/baidu-strategy-shift-ai-revenue-models
